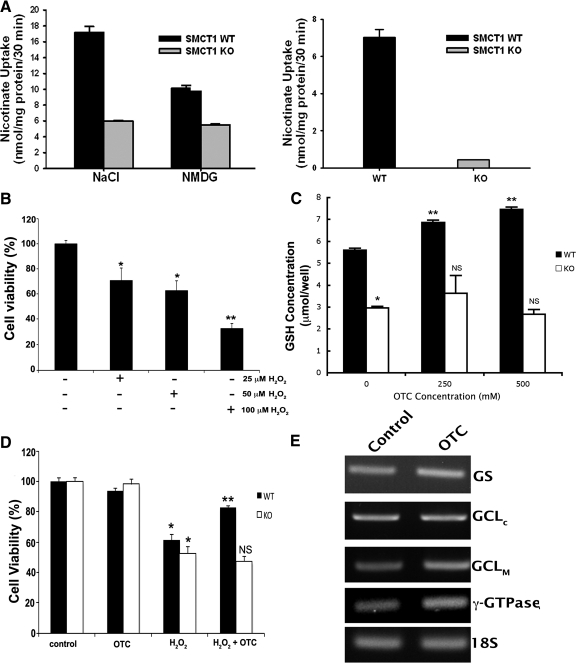
Figure 8.
Functional analysis of Slc5a8 in primary RPE (mRPE) cells isolated from wild type (WT) and Slc5a8-/- (KO) mouse retinas, and OTC-mediated protection of wild type mRPE against H2O2-induced cell death. (A) Wild type and Slc5a8-/- mRPE cells were used for analysis of [14C]-nicotinate (30 μM) uptake. Uptake measurements were made in the presence (NaCl) or absence of Na+ (NMDG). Data in the right panel represent the values for Na+-dependent nicotinate uptake in WT and KO mRPE cells. (B) Dose–response for H2O2-induced oxidative stress/cell death in wild type mRPE. (C) Wild type and Slc5a8-/- mRPE cells were incubated in the presence or absence of two different concentrations of OTC (250 and 500 μM) for 60 minutes, followed by determination of intracellular glutathione concentration (*P < 0.001 compared to WT cells; **P < 0.001 compared to WT cells cultured in the absence of OTC; NS, not significant compared to KO cells cultured in the absence of OTC). (D) Oxidative stress was induced in WT and KO mRPE using H2O2 (25 μM) in the presence or absence of 500 μM OTC. Cell viability was analyzed by trypan blue exclusion assay (*P < 0.01 compared to control cells cultured in the absence of H2O2 and of OTC; **P < 0.01 compared to WT cells cultured in the presence of H2O2; NS, not significant compared to KO cells cultured in the presence of H2O2). (E) RT-PCR analysis of mRNA expression of genes involved in glutathione homeostasis.