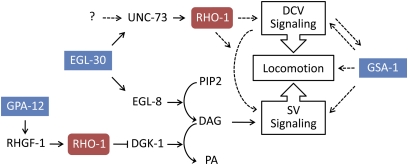
Figure 7 .
Rho GTPase and heterotrimeric G-protein pathway interactions regulating neurotransmission and locomotion. G-protein pathways (blue boxes) interact with Rho GTPase pathways (red boxes) directly (solid arrows) or through indirect or unknown mechanisms (dashed arrows). Rho exists in two separate populations, only one of which interacts with DGK-1 (Hiley et al. 2006; McMullan et al. 2006). The Gαo (GOA-1) pathway negatively regulates Gαq (EGL-30) and synaptic vesicle signaling, but is omitted for clarity (Hajdu-Cronin et al. 1999; Miller et al. 1999; Nurrish et al. 1999). UNC-73 RhoGEF-2 activity (UNC-73) functions downstream of EGL-30 and likely another factor(s) to modulate locomotion through dense core vesicle (DCV) and/or synaptic vesicle (SV) signaling. Constitutive Gαs (GSA-1) pathway activation can compensate for unc-73 RhoGEF-2 mutant locomotion defects, but the mechanism is not known. See the Discussion and references for details (Brundage et al. 1996; Kozasa et al. 1998; Lackner et al. 1999; Reynolds et al. 2005; Schade et al. 2005; Charlie et al. 2006; Hiley et al. 2006; McMullan et al. 2006; Williams et al. 2007; Zhou et al. 2007).