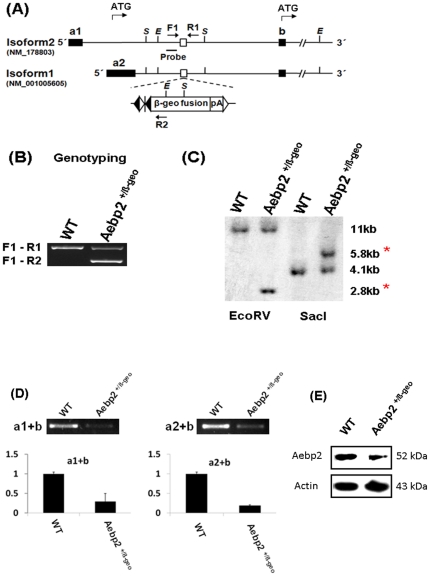
Figure 1. Generation of an Aebp2-knockin allele.
(A) The gene trap vector has inserted into the first intron of Aebp2 gene (empty box). This gene trap vector contains two FRT sites (empty triangle), two loxP sites (black triangle, lox71 and loxP), one splicing acceptor site (vertical line), the β-Geo fusion protein cassette, and a polyadenylation signal. Two alternative START codons are indicated with arrow on top. (B) Genotyping with three primers (F1, R1, R2). PCR amplification with primers F1 and R1 derives a 570-bp product from the wild-type allele (+), whereas PCR with F1 and R2 produces a 304-bp product from the knockin allele (−). (C) Southern blot analysis using genomic DNA (10 µg) from the wild-type (Aebp2+/+) and heterozygote (Aebp2+/β-Geo) after restriction enzyme digestion with EcoRV and SacI. The wild-type and knockin (asterisk) alleles were detected as expected. (D) qRT-PCR analyses with the total RNA from the neonatal brains of the wild-type and heterozygotes confirm the proper truncation of the Aebp2 transcripts by the gene trap vector. (E) Western blotting using the protein extracts from neonatal brains confirmed reduced levels of the AEBP2 protein in the Aebp2+/β-Geo mice relative to the wild-type littermates. The original image for this western result is available as Figure S1.