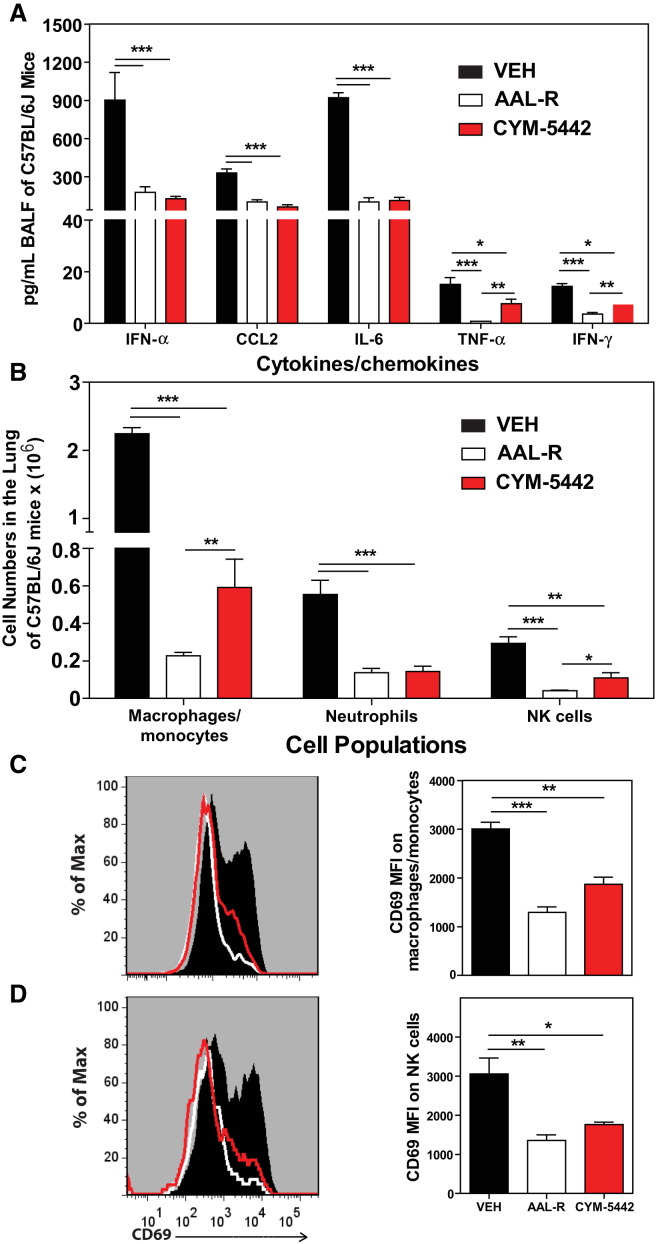
Figure 1.
S1P1 Receptor Agonism Suppresses Early Proinflammatory Cytokine and Chemokine Production and Innate Immune Cell Recruitment during Influenza Virus Infection
Mice were infected with 1 × 104 PFU WSN influenza virus, and vehicle (water), AAL-R (0.2 mg/kg) (1 hr postinfection), or CYM-5442 (2 mg/kg) (1,13, 25, and 37 hr postinfection) were administered i.t. to mice.
(A) Proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines were measured 48 hr postinfection in BALF by ELISA.
(B) Total numbers of innate immune cells were quantified from collagenase-digested lungs by flow cytometry at 48 hr postinfluenza virus infection.
(C) Histograms (left) and mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) (right) of CD69 expression on macrophages was quantified on vehicle, AAL-R-, or CYM-5442-treated mice 48 hr postinfluenza virus infection by flow cytometry staining.
(D) Histograms (left) and MFI (right) of NK cell CD69 expression quantified as in (C).
Data represent average ± SEM from four to mice per group. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.005; ∗∗∗p < 0.0005. Results are representative of greater than six independent experiments. See also Figure S1 and Figure S2.