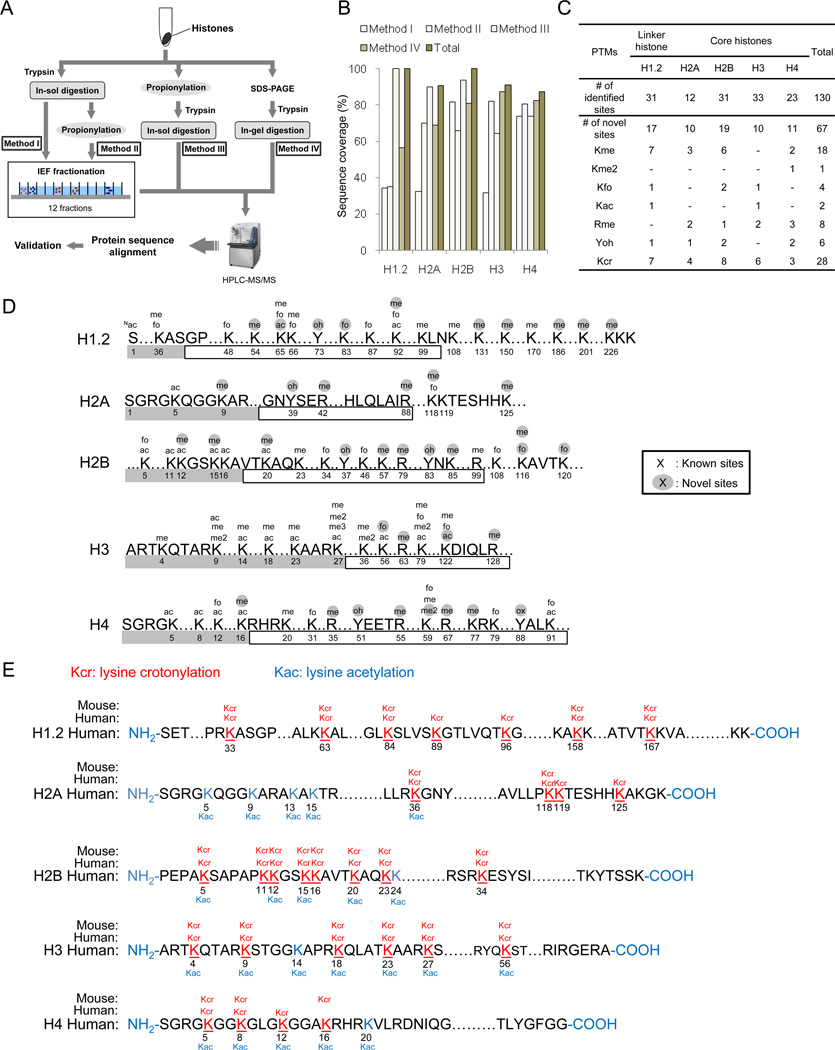
Figure 1.
Experimental strategy and results for identified histone PTM sites. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental design for comprehensive mapping of PTM sites in linker and core histones from HeLa cells. Histone extracts were in-solution trypticly digested without chemical propionylation (Method I), chemically propionylated after in-solution tryptic digestion (Method II), chemically propionylated before in-solution tryptic digestion (Method III), and in-gel digested after SDS-PAGE gel separation. Samples from Methods I and II were further subjected to IEF fractionation to generate 12 fractions. (B) Peptide sequence coverage of linker and core histones in each of the four methods is shown. (C) A table summarizing all the PTM sites identified by this study. Abbreviations: me, monomethylation; me2, dimethylation; me3, trimethylation; fo, formylation; ac, acetylation; oh, hydroxylation; cr, crotonylation. (D) A diagram showing sites of histone PTMs other than Kcr identified in this study. Amino acid residue number is indicated below its sequence. Gray and blank boxes indicate N-terminal and globular core domains, respectively. (E) Illustrations of histone Kcr sites in human HeLa cells and mouse MEF cells. All Kcr sites are shown in red and underlined. Previously reported Kac sites are shown in blue.