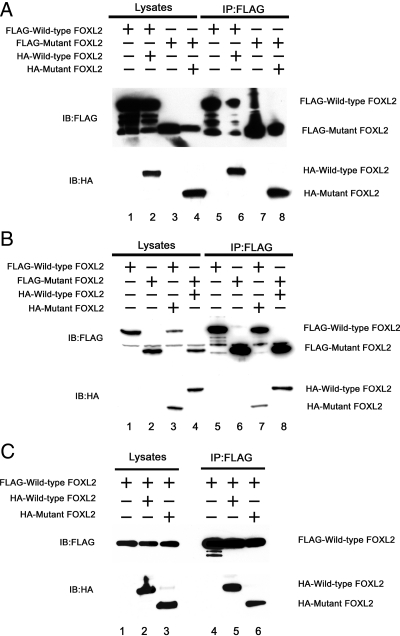
Fig. 2.
Dimerization of wild-type and mutant FOXL2. A, To test for the ability to form homodimers, CHO cells were transiently cotransfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type FOXL2 alone (lane 1), with FLAG-tagged and HA-tagged wild-type FOXL2 (lane 2), with FLAG-tagged mutant FOXL2 alone (lane 3), or with FLAG-tagged and HA-tagged mutant FOXL2 (lane 4). The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using an anti-FLAG antibody (lanes 5–8) and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies to FLAG and HA. FLAG-wild-type FOXL2 coimmunoprecipitates with HA-wild-type FOXL2. Furthermore, FLAG-mutant FOXL2 coimmunoprecipitates with HA-mutant FOXL2. B, To test the ability to form heterodimers, CHO cells were transiently cotransfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type FOXL2 alone (lane 1), FLAG-tagged mutant FOXL2 alone (lane 2), FLAG-tagged wild-type FOXL2 and HA-tagged mutant FOXL2 (lane 3), or with FLAG-tagged mutant FOXL2 and HA-tagged wild-type FOXL2 (lane 4). The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using an anti-FLAG antibody (lanes 5–8) and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies to FLAG and HA. FLAG-wild-type FOXL2 and HA-mutant FOXL2 coimmunoprecipitate, as do HA-wild-type FOXL2 and FLAG-mutant FOXL2. C, To examine whether wild-type FOXL2 has different affinity for wild-type vs. mutant FOXL2, CHO cells were transiently cotransfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type FOXL2 alone (lane 1), FLAG-tagged wild-type FOXL2 and HA-tagged wild-type FOXL2 (lane 2), or FLAG-tagged wild-type FOXL2 and HA-tagged mutant FOXL2 (lane 3). The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using an anti-FLAG antibody (lanes 4–6) and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies to FLAG and HA. FLAG-tagged wild-type FOXL2 had affinity for HA-tagged mutant FOXL2 but slightly less than for HA-tagged wild-type FOXL2.