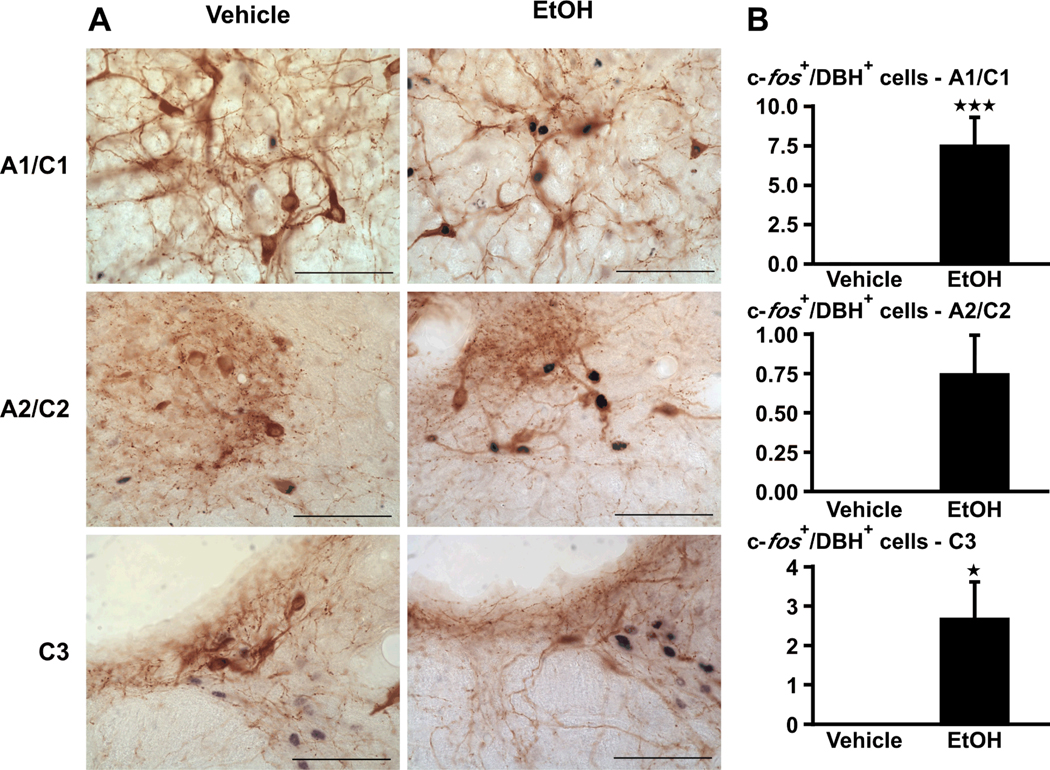
Figure 2.
(A) Acute alcohol (EtOH) increases c-fos signals in the A1–A2/C1–C3 cell region, identified by DBH. Bright-field photographs through the A1–A2/C1–C3 area of brain stem from vehicle controls (left), and rats challenged with alcohol (right). Images show a representation of the double immunohistochemistry that stained c-fos-ir in black and DBH-ir in brown (scale bar = 200 µm). (B) Cell counts were obtained for c-fos immunoreactivity in DBH-ir cells. Mean ± SEM levels of c-fos signals in DBH–ir cells in the A1/C1, A2/C2 and C3 area of 5–6 rats injected with vehicle or alcohol. *, P<0.05; ***, P<0.001.