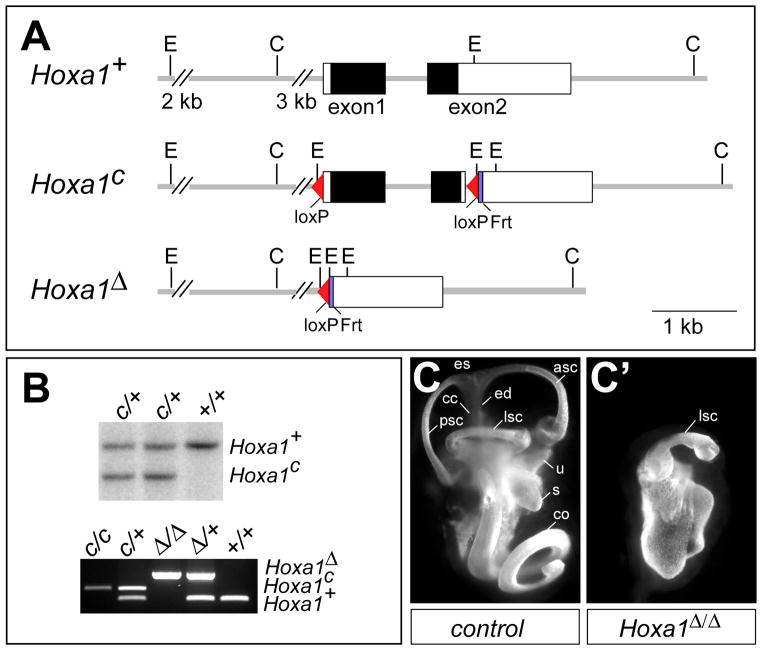
Fig. 1. Hoxa1 targeting and phenotype analysis.
(A) Depiction of Hoxa1 wild-type (Hoxa1+), conditional (Hoxa1c) and deletion (Hoxa1Δ) alleles. The Hoxa1c allele was generated by inserting a 5′ loxP site 200 bp upstream of the Hoxa1 transcription initiation site and a loxP-frt-PolII-Neo-frt cassette 36 bp downstream of the Hoxa1 stop codon. The Neo cassette was removed by recombination, leaving one frt site behind. In the Hoxa1Δ allele, the entire Hoxa1 promoter and coding region are deleted. Black boxes, Hoxa1 coding region; white boxes, UTRs. C, ClaI; E, EcoRI. (B) Upper panel: Southern blot analysis to identify positive Hoxa1c clones. DNA was digested with EcoRI and hybridized with a 5′ external probe to generate an 8.3 kb wt and a 6 kb Hoxa1c band. Lower panel: PCR genotyping to identify the different Hoxa1 alleles. (C, C′) Abnormal inner ear morphology of Hoxa1 mutants. Lateral view of paint-filled inner ears from E15.5 control (C) and Hoxa1Δ/Δ mice (C′). asc, anterior semicircular canal; cc, common crus; co, cochlea; ed, endolymphatic duct; es, endolymphatic sac; lsc, semicircular canal; s, saccule; u, utricle.