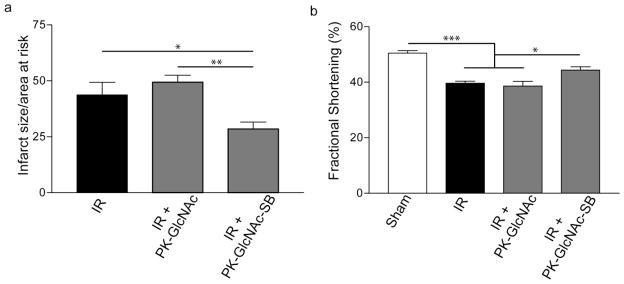
Figure 7. Infarct size reduction and functional improvements seen in PK-GlcNAc-SB treatment following ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Immediately following IR, particles were injected directly into the injured myocardium. Three days following surgery, echocardiography was performed and heart cross sections analyzed for infarct size. (a) The ratio of infarct size to area at risk was calculated for the treatment groups. PK-GlcNAc treatment had no significant effect, but PK-GlcNAc-SB treatment significantly decreased infarct size compared to both treatment groups (mean±SEM, n=5; *p<0.05, **p<0.01; ANOVA followed by Newman-Keul multiple comparison post-test). (b) Fractional shortening calculated from echocardiographic measurements demonstrated a significant decrease in function in IR animals compared to sham. There was no significant improvement seen with PK-GlcNAc, though PK-GlcNAc-SB treatment improved function compared with other IR groups. (n=4 for sham n>7 for IR groups). Data are mean±SEM. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001. ANOVA followed by Tukey post-test.