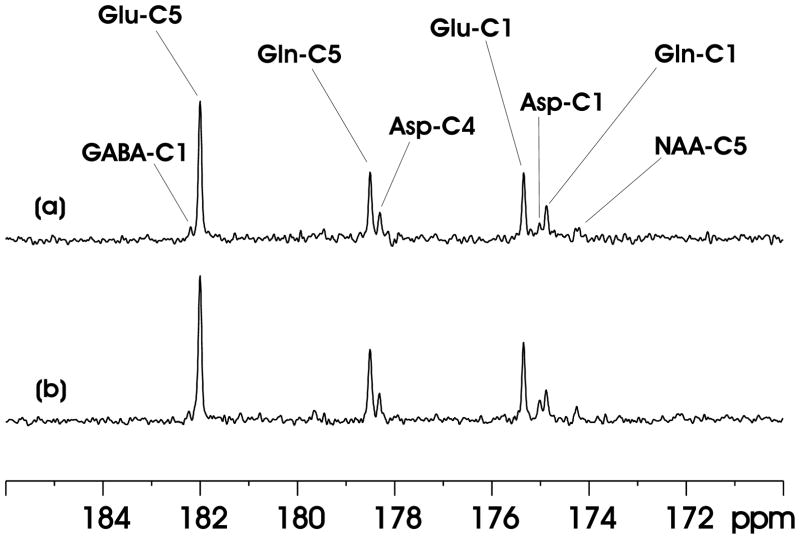
Fig. 3.
(a) A proton-decoupled localized 13C MRS spectrum of the carboxylic/amide spectral region acquired from the rat brain at 11.7 Tesla during intravenous infusion of [2,5-13C2]glucose. Voxel size = 8.5 × 6 × 8.5 mm3. No. of averages = 30. Ernst’s pseudo stochastic decoupling scheme was used with γB2 = 498 Hz at the center of the spectroscopy voxel. lb = −1, gb = 0.06. GABA-C1 = γ-amminobutyric acid C1, Glu-C5 = glutamate C5, Gln-C5 = glutamine C5, Asp-C4 = aspartate C4, Glu-C1 = glutamate C1, Asp-C1 = aspartate C1, Gln-C1 = glutamine C1, NAA-C5 = N-acetylaspartate C5. (b) In vivo 13C MRS spectrum acquired using the proposed windowed stochastic decoupling sequence (Fig. 2(c, d)). The peak RF amplitude of the windowed stochastic decoupling sequence is 707 Hz with decoupling power ( ) at 51.4% of that used in (a). All other data acquisition and processing parameters are the same as in (a).