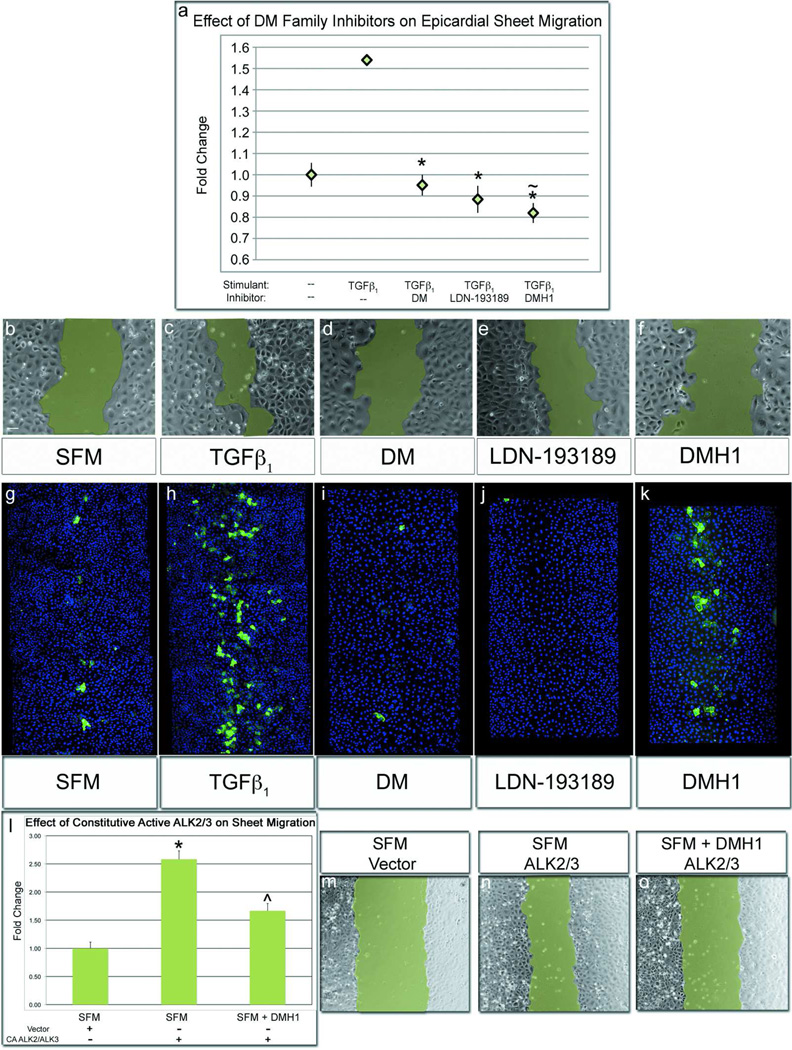
Figure 4.
DMH1 strongly inhibits epicardial sheet movement, but not SMA expression. Epicardial sheet migration rate was assessed by wound healing assays with representative images of wounds at six hours in b–f. a,c) Wounding epicardial sheets in the presence of TGFβ1 significantly increased sheet migration rate in comparison cells wounded in medium. a,d–e) Epicardial wounds cultured with TGFβ1 and concurrently treated with DM/LDN-193189 healed at medium-equivalent rates. a,f) Interestingly, sheets wounded with TGFβ1-and the BMP inhibitor, DMH1, healed at a rate significantly slower than unstimulated sheets. g) Epicardial sheets wounded in medium spontaneously expressed SMA after an 18-hour incubation. h) When wounds were cultured with TGFβ1, SMA expression was strongly increased. i–j) Conversesly, when sheets cultured with TGFβ1 and treated with DM/LDN-193189, SMA expression was inhibited. e) DMH1 marginally inhibited TGFβ1-stimulated SMA expression. l, n) Epicardial sheet migration was strongly stimulated by constitutively active ALK2/3 l,o) Migration was modestly inhibited by treatment of constitutively active-ALK2/3 cells with DMH1, which differs from the significant inhibition that DMH1 exerts on sheet migration in wildtype cells. [n≥8 wounds; Scale bar=50µm; (*p<0.001 from TGFβ1 stimulated cells; ~p<0.001 from untreated cells; ^~p<0.001 from untreated CA-ALK2/3); CA-ALK2/3=Constitutively Active-ALK2/3].