Figure 2.
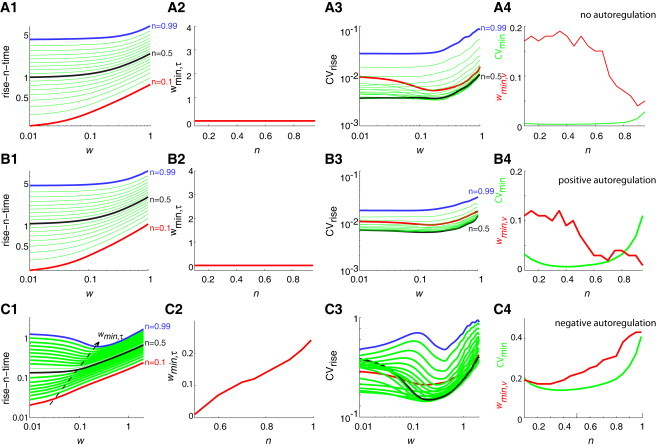
Effects of positive and negative autoregulation (stochastic simulations). Simulation results in the absence of autoregulation (A), in the presence of positive autoregulation (B), and in the presence of negative autoregulation (C). (A1–C1) Variation of the mean rise-n-times (in units of generation times, shown in log scale) for different values of w and n. Here the noise level parameters are μ = 0.007 and σ = 4, ν = 3 × 10−4, w is iterated with a step-size Δw = 0.01 (shown in log scale), the scaled time step was Δτ = 0.001, and n is iterated inside the interval 0.1–0.99 with Δn = 0.05. All the statistical quantities were computed over 105 stochastic realizations (see Theory). (Red lines) n = 0.1. (Black lines) n = 0.5. (Blue lines) n = 0.99. In panel C1 and particularly for n > 0.3, the rise-n-time showed a minimum at wmin,τ < 10−2. (A2–C2) Value of wmin,τ as a function of n. (A3–C3) Coefficient of variation of the rise-n-times (shown in log scale) as a function of w (shown in log scale) for different values of n. The value of CV attains a minimum when w → wmin,τ. Note that wmin,τ ≠ wmin,ν. (A4–C4) Both the parameters CVmin (green) and wmin,ν (red) are shown here as a function of n. The minimum value of CVmin occurs for different values of n in the negative and positive autoregulation cases. The noisy red curves can be attributed to the difficulty in defining a minimum w point for several of the curves in panels A3–C3.
