Figure 1.
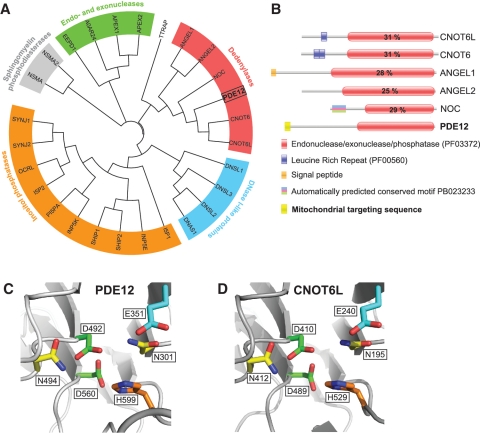
Computational analysis of PDE12. (A) The unrooted classification tree of human EEP proteins. The sequences of the catalytic domain of all human proteins of the EEP family (PF03372) were extracted from the Pfam database (see Supplementary Table S1 for details) and aligned using ClustalW2. Five major subgroups identified are indicated on the tree: inositol phosphatases (orange), Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterases (grey), Endo- and exonucleases (green), DNase I-like proteins (blue) and Deadenylases (red). (B) Domain architecture of confirmed and putative human deadenylases of the EEP family. Functional domains of human proteins of the ‘Deadenylases’ subgroup identified in (A) are schematically represented. The position of the EEP domain is represented in each protein by a red box containing the percentage of identity between this domain and that of PDE12. (C and D) Comparison of the active site structure of PDE12 and other EEP deadenylases. The active site structural motif of PDE12 (C) predicted based on the known crystal structure of the homologous EEP deadenylase CNOT6L (D) using the 3D-Jury algorithm (42) was modelled using the MODELLER 9v1 software (43).