Abstract
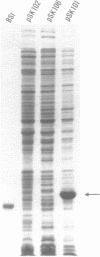
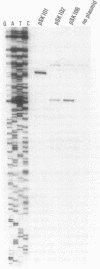
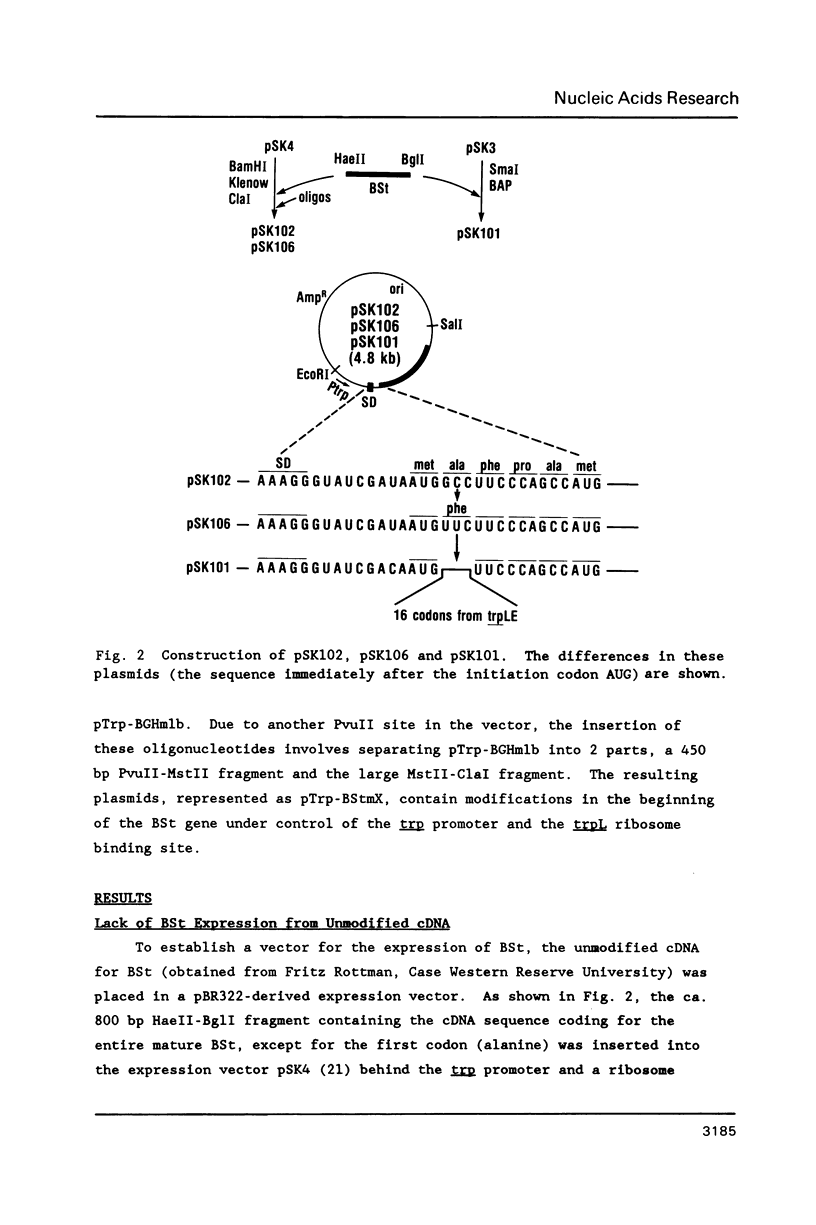
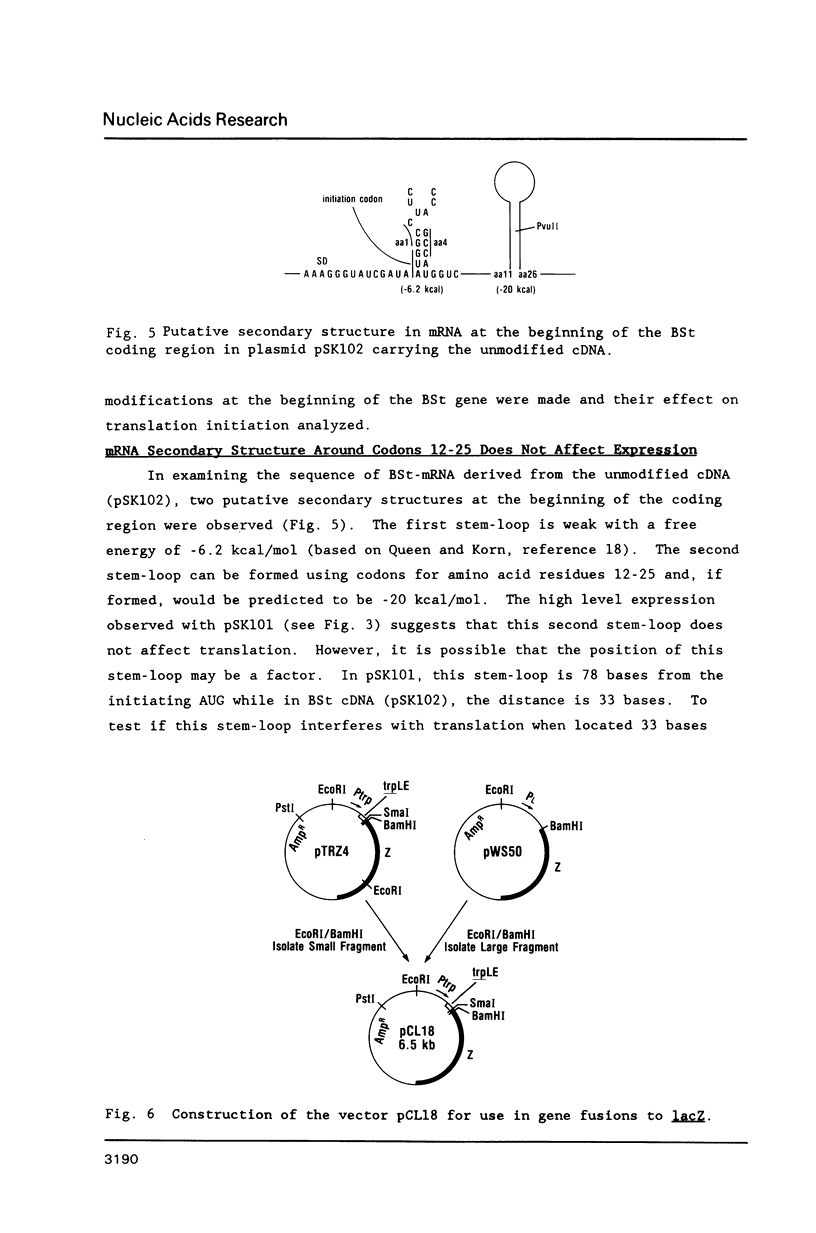
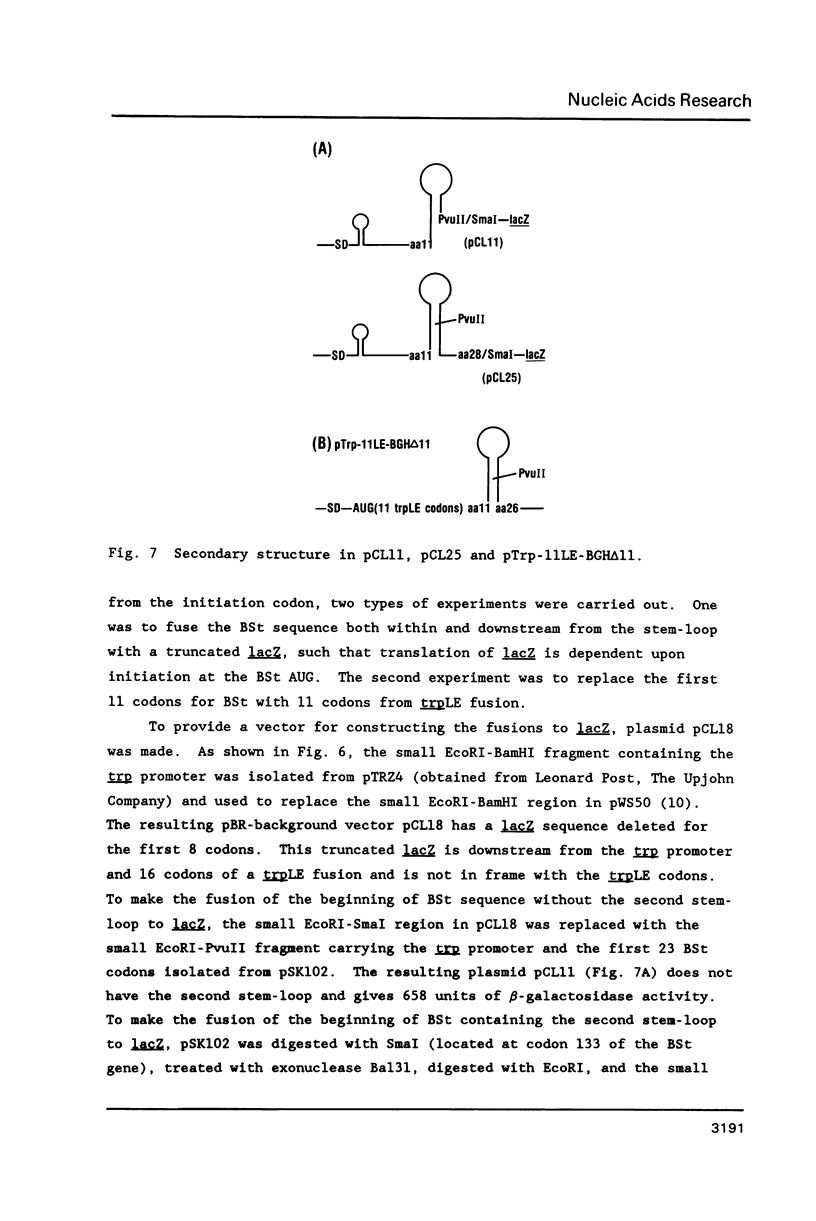
We have studied the expression of bovine somatotropin (BSt) to gain more understanding of various factors affecting translation in E. coli. The unmodified cDNA coding for mature bovine somatotropin does not produce significant amounts of BSt in E. coli using a pBR322-derived vector. However, a translation fusion with 16 codons from trpLE in front of BSt cDNA results in greater than 20% of total cell protein as the fusion product. Analysis of transcription by measuring the rate and integrity of the mRNA confirms that a post-transcriptional event is responsible for the poor expression of the BSt cDNA. There are two potential stem-loop structures in the 5' region of the mRNA which may interfere with translation. To study their effect on translation, lacZ fusions and oligonucleotide mutagenesis were carried out. The results demonstrate that the secondary structure involving the initiation codon blocks translation initiation. Removal of this stem-loop results in a 100-fold increase in BSt expression. However, the expression level is still low, amounting to only 0.5-1% of total cell protein. High level expression can be obtained by replacement of the beginning sequence of BSt cDNA with trpLE codons. These results suggest that in addition to the secondary structure, the nucleotide sequence or amino acid context within the beginning of BSt is incompatible with one of the steps in translation initiation.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baughman G., Nomura M. Localization of the target site for translational regulation of the L11 operon and direct evidence for translational coupling in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):979–988. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90555-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. N., Schweingruber M. E., Brown K. D., Squires C., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of the promoter--operator region of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 15;121(2):113–137. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(78)80001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogosian G., Somerville R. L., Nishi K., Kano Y., Imamoto F. Transcription of the trpR gene of Escherichia coli: an autogeneously regulated system studied by direct measurements of mRNA levels in vivo. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(2):244–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00330675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Inouye M., Nakamura K. Mutations upstream of the ribosome-binding site affect translational efficiency. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., de Crombrugghe B., Adhya S., Gottesman M. Bacteriophage lambda hin function. II. Enhanced stability of lambda messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 25;138(4):731–743. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Jolly C. T., Mural R. J. Interference with the expression of the N gene function of phage lambda in a mutant of Escherichia coli. Virology. 1973 Jan;51(1):216–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George H. J., L'Italien J. J., Pilacinski W. P., Glassman D. L., Krzyzek R. A. High-level expression in Escherichia coli of biologically active bovine growth hormone. DNA. 1985 Aug;4(4):273–281. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Gabay J., Débarbouillé M., Schwartz M. A role for mRNA secondary structure in the control of translation initiation. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):616–618. doi: 10.1038/295616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looman A. C., Bodlaender J., de Gruyter M., Vogelaar A., van Knippenberg P. H. Secondary structure as primary determinant of the efficiency of ribosomal binding sites in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5481–5497. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miozzari G. F., Yanofsky C. Translation of the leader region of the Escherichia coli tryptophan operon. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1457–1466. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1457-1466.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson L. M., Stormo G. D., Niece R. L., Reznikoff W. S. lacZ translation initiation mutations. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 25;177(4):663–683. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R., Tinoco I., Jr, Jacobson A. B. Small changes in free energy assignments for unpaired bases do not affect predicted secondary structures in single stranded RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):341–349. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Korn L. J. A comprehensive sequence analysis program for the IBM personal computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):581–599. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. Globin mRNA sequences: analysis of base pairing and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):985–1002. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner B. E., Hsiung H. M., Belagaje R. M., Mayne N. G., Schoner R. G. Role of mRNA translational efficiency in bovine growth hormone expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5403–5407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Sias S., Adelman J., de Boer H. A., Hayflick J., Jhurani P., Goeddel D. V., Heyneker H. L. Efficient bacterial expression of bovine and porcine growth hormones. DNA. 1983;2(1):37–45. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1983.2.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisk W. P., Chirikjian J. G., Lautenberger J., Jorcyk C., Papas T. S., Berman M. L., Zagursky R., Court D. L. A plasmid vector for cloning and expression of gene segments: expression of an HTLV-I envelope gene segment. Gene. 1986;48(2-3):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Remaut E., Fiers W. Alterations upstream from the Shine-Dalgarno region and their effect on bacterial gene expression. Gene. 1985;36(3):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessier L. H., Sondermeyer P., Faure T., Dreyer D., Benavente A., Villeval D., Courtney M., Lecocq J. P. The influence of mRNA primary and secondary structure on human IFN-gamma gene expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7663–7675. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. R., Boss M. A., Patel T. P., Emtage J. S. The influence of messenger RNA secondary structure on expression of an immunoglobulin heavy chain in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3937–3950. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]