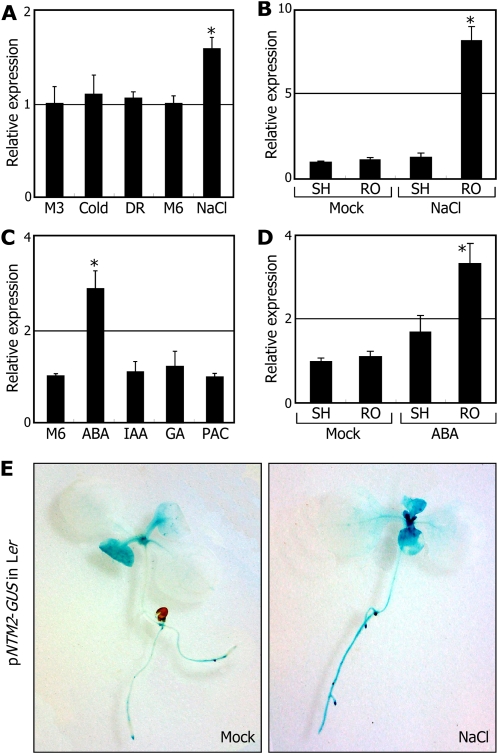
Figure 2.
The NTM2 gene is induced by high salt. Transcript levels were determined by qRT-PCR. Biological triplicates were averaged. Error bars indicate se. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test (* P < 0.01). Two-week-old plants grown on MS-agar plates were used for extraction of total RNA or subsequent treatments. A, Effects of abiotic stress conditions on NTM2 gene transcription. Plants were exposed to cold (4°C, 3 h), drought (DR; 3 h), or NaCl (150 mm, 6 h). Whole plants were used for extraction of total RNA. M3 and M6, Mock treatments for 3 and 6 h, respectively. B, Effects of high salinity on NTM2 gene transcription in the shoots (SH) and roots (RO). Plants were soaked for 6 h in MS liquid cultures supplemented with 150 mm NaCl, and the shoot and root samples were harvested separately for extraction of total RNA. C, Effects of growth hormones on NTM2 gene transcription. Plants were transferred to MS liquid cultures containing appropriate concentrations of growth hormones, such as ABA (50 μm, 6 h), IAA (20 μm, 6 h), GA (50 μm, 6 h), or PAC (50 μm, 6 h). Whole plants were used for extraction of total RNA. D, Effects of ABA on NTM2 gene transcription in the shoots and roots. Plants were treated with ABA as described in C, and the shoot and root samples were harvested separately for extraction of total RNA. E, Effects of high salinity on the promoter activities of the NTM2 gene. Two-week-old transgenic plants expressing the pNTM2-GUS fusion grown on MS-agar plates were incubated for 6 h in MS liquid cultures supplemented with 150 mm NaCl and subjected to GUS staining.