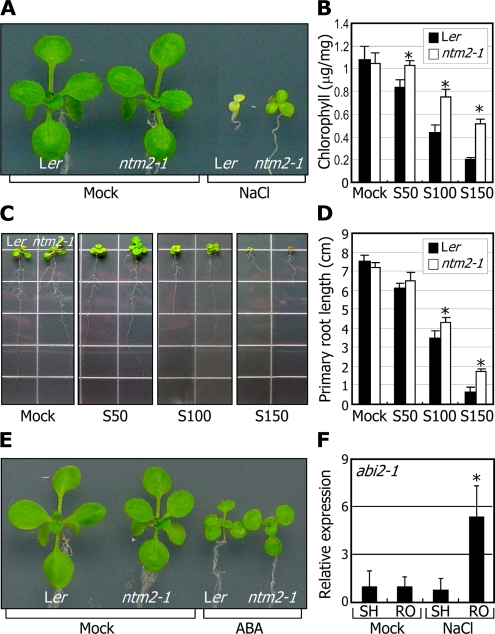
Figure 3.
The ntm2-1 mutant exhibits reduced sensitivity to high salinity. A, Effects of high salinity on ntm2-1 seedling growth. Three-day-old seedlings grown on MS-agar plates were transferred to fresh MS-agar plates supplemented with 150 mm NaCl and further grown for 2 weeks. B, Measurements of chlorophyll contents. Aerial parts of 2-week-old seedlings grown on MS-agar plates containing various concentrations of NaCl were used for extraction of chlorophylls. Ten measurements were averaged. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test (* P < 0.01). Error bars indicated se. S50, S100, and S150, NaCl at 50 mm, 100 mm, and 150 mm, respectively. C and D, Effects of high salinity on primary root growth. Three-day-old seedlings grown on MS-agar plates were transferred to fresh MS-agar plates supplemented with various concentrations of NaCl and further grown for 10 d (C). Primary root lengths of 20 seedlings were measured and averaged (D). Error bars represent se (t test; * P < 0.01). E, Effects of ABA on ntm2-1 seedling growth. Plants were treated as described in A, but 0.6 μm ABA was used instead of NaCl. F, Effects of high salinity on NTM2 gene transcription in the abi2-1 mutant. Two-week-old plants grown on MS-agar plates were transferred to MS liquid cultures supplemented with 150 mm NaCl and soaked for 6 h. The shoot (SH) and root (RO) samples were harvested separately for extraction of total RNA. Levels of the NTM2 transcripts were determined by qRT-PCR. Biological triplicates were averaged. Error bars indicate se (t test; * P < 0.01).