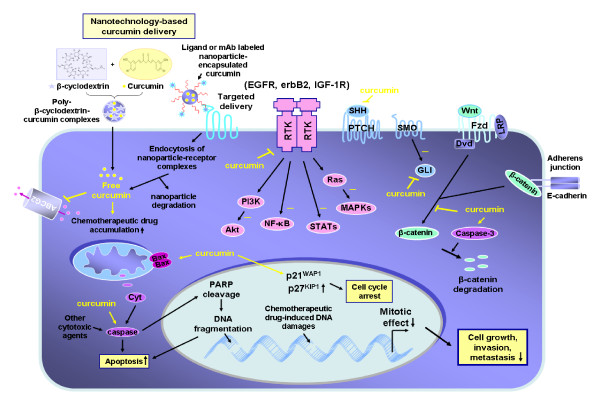
Figure 1.
Tumorigenic cascades initiated by different growth factors in cancer cells and the anticarcinogenic effects induced by dietary curcumin on the transduction signaling elements. The inhibitory effect of curcumin on the expression and/or activity of EGFR, erbB2, IGF-1R, and their downstream signaling elements, sonic hedgehog (SHH/SMO/GLIs), Wnt/β-catenin and ATP-binding cassette multidrug transporters such as ABCG2 in cancer cells are indicated. Moreover, the enhanced expression of p21WAP1 and p27KIP1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and inhibition of mitotic effects induced by curcumin resulting in a cell cycle arrest and reduced expression levels of different gene products involved in the growth, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells as well as the activation by curcumin of mitochondrial factors and caspase pathway-induced apoptosis are also indicated. In addition, the scheme also shows novel nanotechnology-based curcumin delivery systems consisting of using either a poly(β-cyclodextrin)-curcumin complex formulation, or a polymeric micelle-encapsulated curcumin labeled with a ligand or monoclonal antibody (mAb) that specifically interacts with a receptor expressing by cancer cells for the selective targeting of curcumin are also illustrated.