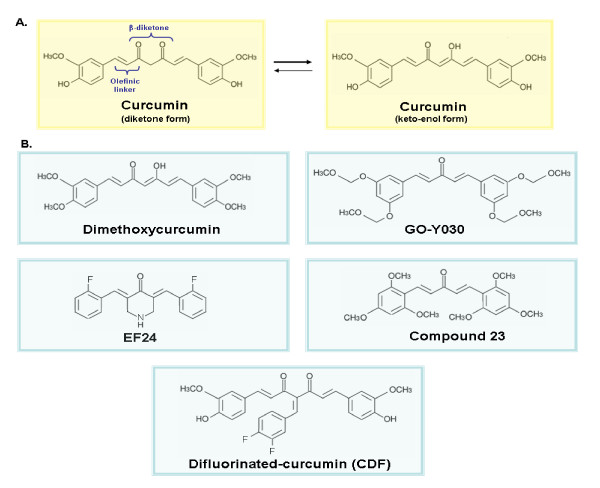
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of naturally occurring curcumin and its novel synthetic analogs. The scheme shows (A) The diketone and keto-enol forms of curcumin. Curcumin exists as an equilibrium mixture of two tautomeric forms in solution. The enol structure of curcumin, which is stabilized by intramolecular H-bonding, is the most energetically stabilized and favored form; (B) chemical structures of novel synthetic analogs of dietary curcumin (dimethoxycurcumin, GO-Y039, EF24, compound 23 and difluorinated-curcumin "CDF") showing improved chemical stability and anticarcinogenic properties on different cancer cell lines.