Figure 1.
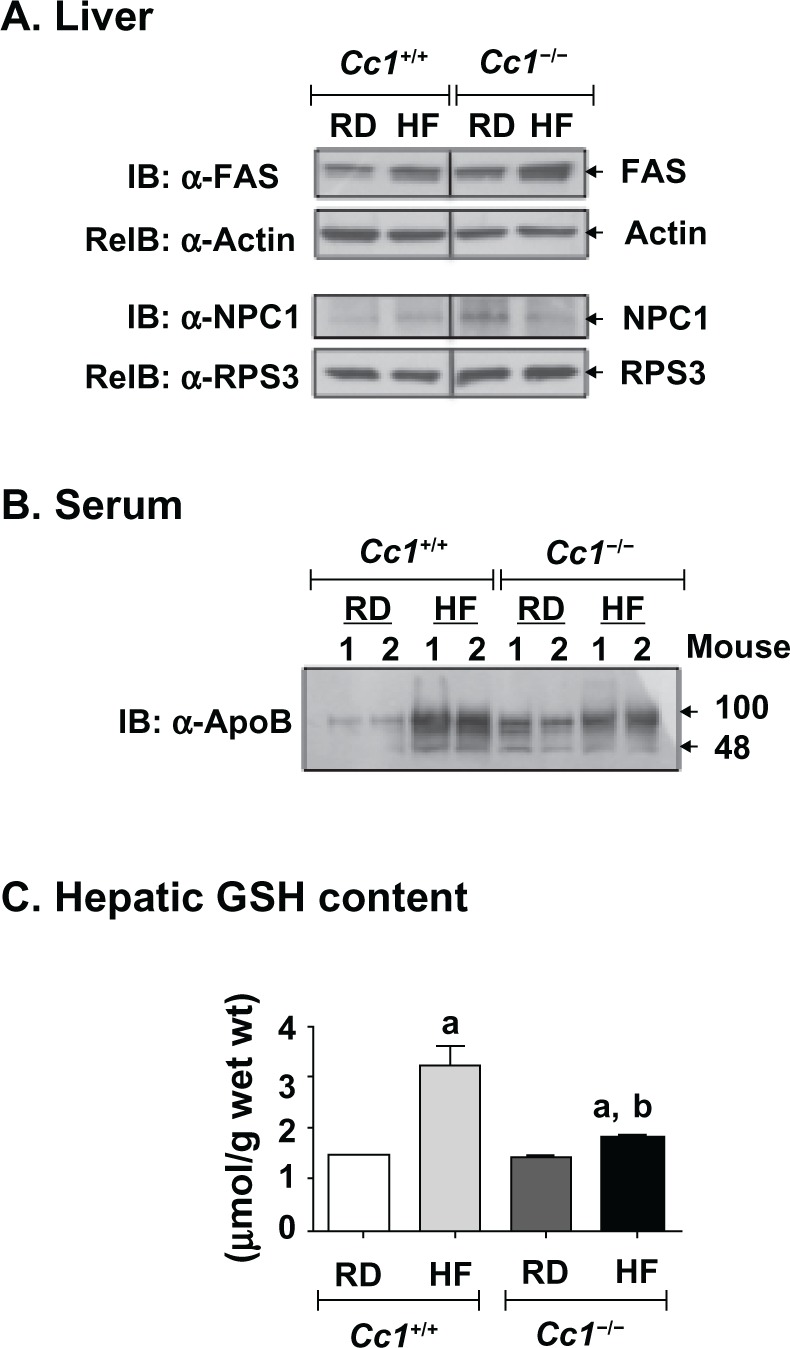
Effect of HF diet on proteins related to hepatic lipid metabolism and on hepatic glutathione (GSH) levels in male Cc1+/+ and Cc1−/− mice. Male wild-type Cc1+/+ and Cc1−/− mice were fed a regular chow (RD) or a HF diet for 3 months, starting at 3 months of age. A) Livers were then removed and analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with α-FAS and α-NPC1, followed by reimmunoblotting (reIB) with α-actin and α-RPS3 antibodies, respectively, to normalize for the amount of proteins loaded, as described in Materials and Methods. The gel represents at least 3 mice per feeding group. B) Serum (10 μg) was analyzed, as above, by immunoblotting using α-ApoB antibody to detect ApoB100 and ApoB48 proteins. Although 2 mice are included in the figure, these experiments were performed on at least 5 mice per feeding group. C) Effect on hepatic GSH levels. N > 7 mice per feeding group. Values are mean ± SEM. aP < 0.005 HF versus RD. bP < 0.05 Cc1−/− versus Cc1+/+ in the same feeding group.
Abbreviations: Cc1−/−, global Ceacam1 null mouse; Cc1+/+, wild-type mouse from the same genetic background as Cc1−/− mice; RD, regular diet; HF, high-fat diet; FAS, fatty acid synthase; NPC1, niemann Pick type C1; ApoB, apolipoprotein B; GSH, glutathione; IB, immunoblotting; reIB, reimmunoblotting.
