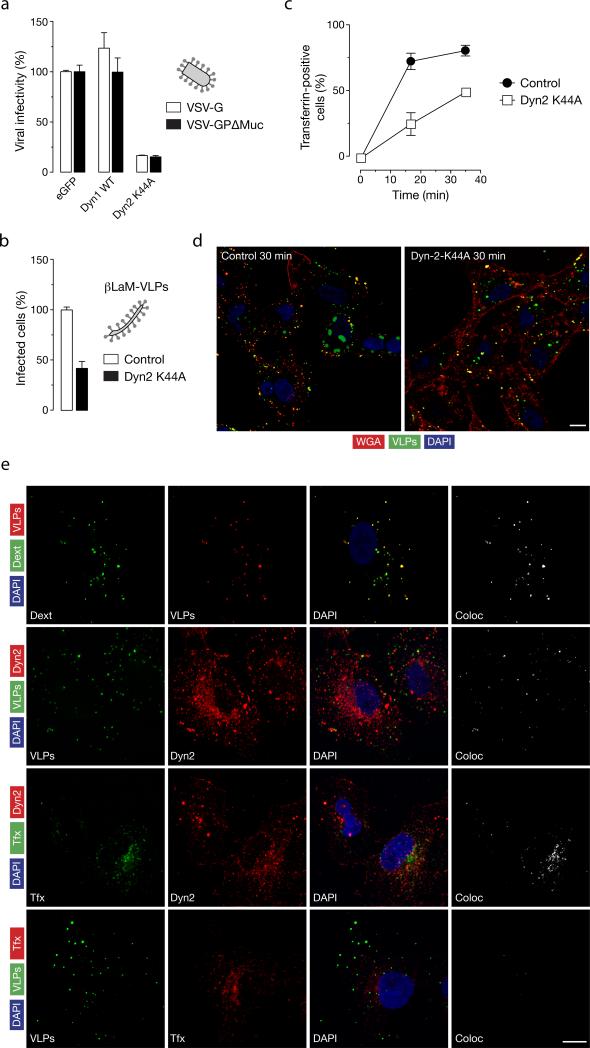
Figure 7. Role of dynamin in EBOV-GPΔMuc-dependent viral uptake and infection.
(A) Expression of dominant-negative dynamin-2 inhibits VSV-GPΔMuc infection. Vero cells expressing eGFP or a dominant-negative dynamin-2 protein (Dyn2 K44A) plasmids were exposed to luciferase-expressing VSV-G or VSV-GPΔMuc. FACS-sorted eGFP-positive cells were assayed for luciferase activity to quantitate infection. Infection is normalized to the control vector cotransfected with eGFP for both viruses. (B) Expression of Dyn2 K44A inhibits entry by βLaM-VLPs. Vero cells transfected with either a control vector plasmid or a plasmid expressing Dyn2 K44A were exposed to βLaM-VLPs, and entry was determined by flow cytometry. (C) Dyn2 K44A inhibits transferrin uptake. Vero cells expressing a Dyn2-K44A-eGFP fusion protein were pulsed with 1 μg/mL Alexa-647-labeled transferrin for the indicated times and VLP uptake was assessed by flow cytometry. (D) Effect of Dyn2 K44A expression on uptake of EBOV VLPs. Representative maximal Z projections of cells transfected with eGFP or Dyn2-K44A-eGFP and exposed to RFP-EBOV VLPs at 37°C for 30 min are shown. Scale bars, 5 μM (E) Endogenous dynamin-2 colocalizes with EBOV VLPs. Vero cells were exposed to the indicated ligands or eGFP/RFP-VLPs for 10 min at 37°C, and then fixed and visualized by confocal fluorescence microscopy. Endogenous dynamin was detected by staining with anti-dynamin primary antibody and an Alexa 594-conjugated secondary antibody. Scale bars, 10 μM. (A-C) Means +/-SD of three replicates are shown.