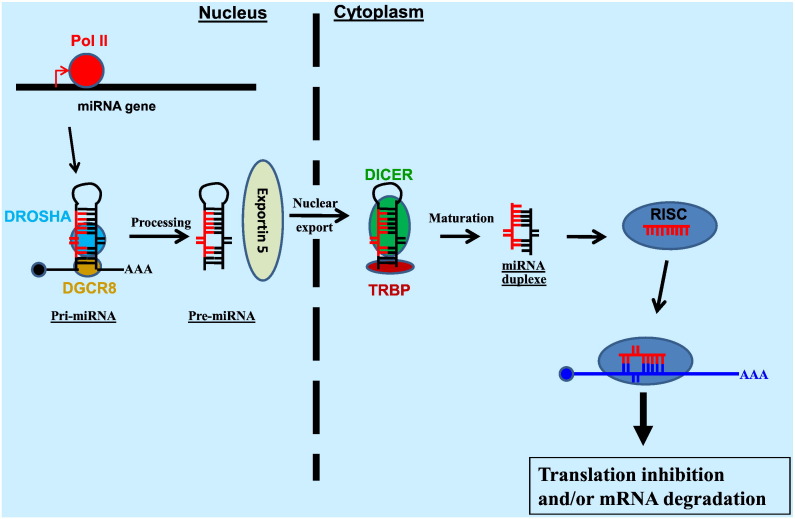
Fig. 1.
miRNA biogenesis and function. A miRNA gene is transcribed by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) to generate the primary miRNA (pri-miRNA). In the nucleus, the pri-miRNA is cleaved by the RNase III endonuclease Drosha to produce a ~ 70 nt precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA). Exportin-5 transports the pre-miRNA to the cytoplasm, where it is cleaved by another RNase III endonuclease, Dicer, together with TRBP, to produce the mature miRNA duplex. The miRNA duplex is then loaded on the Argonaute-containing RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) where one strand is retained as a guide strand to regulate the translation and/or degradation of target mRNA via imperfect basepairing recognition while the other passenger strand is discarded.