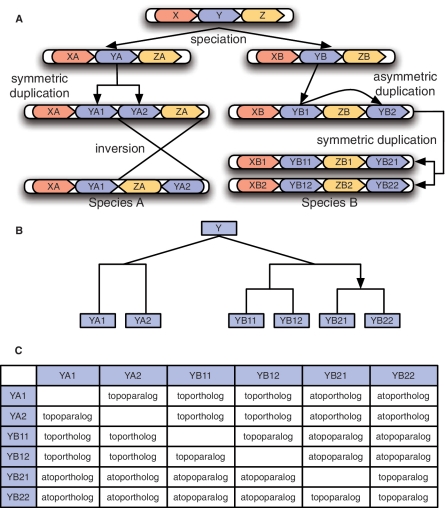
Figure 2:
A hypothetical evolutionary scenario in which we distinguish between classes of orthologs. (A) A speciation event occurs, creating species A and B. The genome of species A undergoes an undirected duplication (a tandem duplication of gene YA) followed by an inversion. Meanwhile, a directed duplication (a segmental duplication of gene YB) followed by a whole genome duplication event occurs within species B. (B) The evolutionary tree for the descendants of gene Y. The top V-shaped split represents a speciation event, while the rectangular splits represent duplications. For the one directed duplication in the tree, the arrow points towards the target copy of the duplication event. (C) The evolutionary terms used to describe the relationship between each pair of extant genes. Note that the inversion event in species A does not impact the evolutionary relationships.