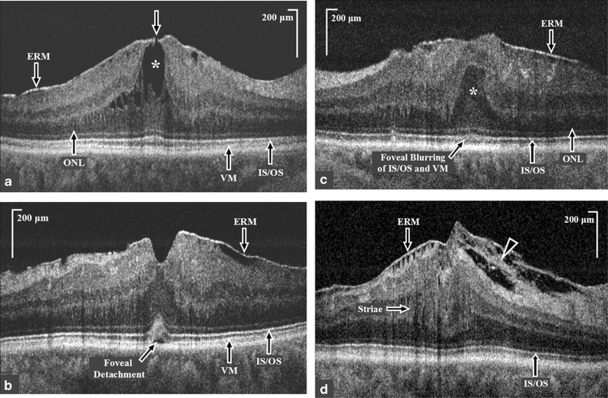
Figure 2.
High-resolution Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography (FD-OCT) B-scan macular images through the fovea of eyes with idiopathic epiretinal membrane (ERM). (a) High-resolution FD-OCT image through the fovea of an eye with BCVA of 20/20, (group 1) showing a lamellar hole (white arrow) with cystoid spaces (white asterisk) in the outer nuclear layer (ONL), and a normal inner segment-outer segment (IS/OS) junction of the photoreceptor layer. Central foveal thickness was 229 μm on FD-OCT, whereas central macular thickness on Stratus OCT was 408 μm. (b) High-resolution FD-OCT image of an eye with BCVA of 20/25 (group II) showing partially intact foveal depression, an increased convexity and blurring of the foveal IS/OS junction and Verhoeff's membrane (VM) and a foveal detachment. (c) High-resolution FD-OCT image of an eye with BCVA of 20/50 showing the presence of epiretinal membrane (ERM), anterior herniation of the outer nuclear layer (ONL; white asterisk) at the fovea and blurring of the foveal IS/OS junction and VM. (d) High-resolution FD-OCT extra-foveal image of an eye with BCVA of 20/50 showing the presence of ERM with tethering of the nerve fiber layer (white arrow head) and striae of the inner retinal layers (white arrow) and a normal IS/OS junction.