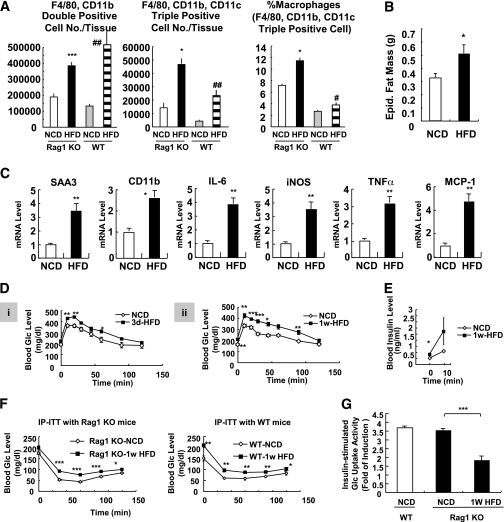
FIG. 6.
Rag1 KO mice develop insulin resistance with increased macrophage activation in 1 week of HFD. A: Macrophage infiltration and M1 polarization were increased by short-term HFD. Rag1 KO mice were treated with HFD for 1 week and killed, and epididymal adipose tissues were taken for further analyses. Total macrophages (double positive; F4/80+, CD11b+) and CD11c+ macrophages (triple positive cells; F4/80+, CD11b+, CD11c+) were increased in adipose tissue in 1 week of HFD. *P < 0.05 KO-NCD vs. KO HFD; ***P < 0.001 KO-NCD vs. KO HFD; #P < 0.05 wild-type (WT)-NCD vs. WT HFD; ##P < 0.01 WT-NCD vs. WT HFD. n = 6. B: Epididymal (Epid.) adipose tissue mass in NCD and 1-week HFD-treated Rag1 KO mice. C: Expression of inflammatory genes was promoted in 1-week HFD-fed Rag1 KO mice. mRNA levels of inflammatory genes from epididymal adipose tissue were measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis. D–F: HFD rapidly induces systemic insulin resistance in Rag1 KO mice. D: Rag1 KO mice (8 weeks old, male) were treated with NCD or HFD for 3 days (3d) (i) or 1 week (1w) (ii) and subjected to oral glucose (Glc) tolerance test. E: Serum insulin levels of Rag1 KO mice treated with NCD or HFD (for 1 week) during oral glucose tolerance. 0 min, before glucose injection; 10 min, 10 min after glucose injection. F: WT or Rag1 KO mice were treated with NCD or HFD for 1 week and subjected to insulin tolerance test with intraperitoneal injection of insulin (IP-ITT). Blood glucose levels were measured at 0, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min after insulin (0.4 unit/kg) injection. G: Glucose-uptake assays using primary adipocytes from mice treated with NCD or HFD for 1 week. iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; SAA3, serum amyloid A3. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.