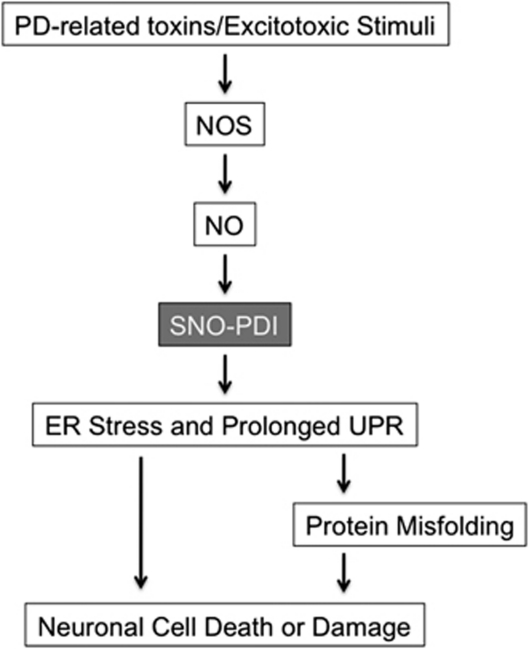
Figure 3.
Possible signaling pathways whereby SNO-PDI contributes to protein misfolding and neuronal damage. In PD, mitochondrial dysfunction caused by pesticides, herbicides, or other environmental toxins can trigger NO and ROS production, possibly via mitochondrial pathways and the NMDAR/Ca2+ cascade.12, 31, 94, 95 NO produced by NOS reacts with sulfhydryl groups of PDI to form SNO-PDI, inhibiting its isomerase and chaperone activities. SNO-PDI formation causes ER stress and a prolonged UPR, and thereby contributes to neuronal cell injury, in part, by triggering accumulation of misfolded proteins