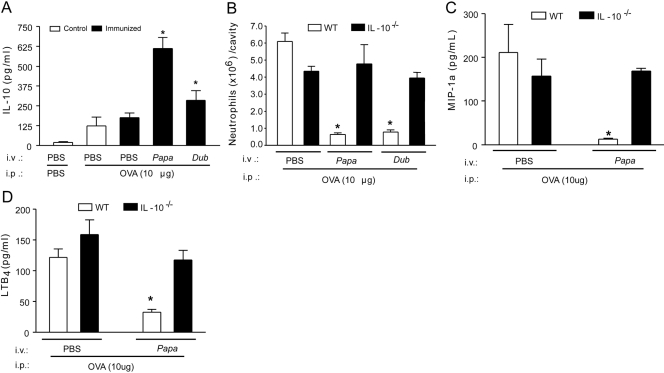
Figure 2.
The anti-inflammatory effect of P. papatasi and P. duboscqi salivary extracts depends on IL-10 production. Wild-type (WT) and IL-10−/− mice were immunized against OVA or sham-immunized mice (Control). Mice were treated with PBS or SGE from P. papatasii or P. duboscqi vector (one salivary gland/i.v./animal) 48 h before i.p. challenge with PBS or OVA (10 μg). Six hours after challenge, peritoneal exudates were collected, and we determined the effect of SGE pretreatment on IL-10 levels (A) in wild-type mice and the effect of P. papatasii on wild-type and IL-10−/− mice upon neutrophil migration (B), MIP-1α (C), and LTB4 (D) production. Data are the mean ± sem and are representative of two experiments; n = 4–6 per group; *, P < 0.05, compared with the PBS-pretreated, OVA-immunized group and challenge with OVA.