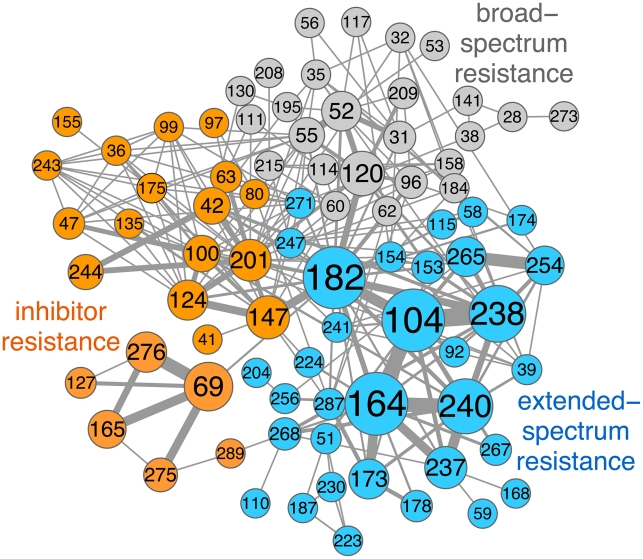
Figure 1. The TEM coevolution network and its communities.
The network was constructed based on frequencies of co-occurring mutated residue positions in 363 mutant TEM β-lactamase sequences. Node size is proportional to how well connected a node is to its neighbors and how many neighbors it has (weighted degree centrality, Methods). Link thickness is proportional to the number of sequences in our database in which both positions are mutated, normalized by the number of sequences in which only one or the other position is mutated (Methods). Node (residue) numbers are shown in Ambler notation. The Clauset community-finding algorithm [31] identified three major communities, corresponding to three Bush-Jacobi β-lactamase phenotype classes: broad-spectrum antibiotic resistance or 2b (gray), extended-spectrum antibiotic resistance or 2be (blue) and inhibitor resistance or 2br (orange). Mutated positions with phenotypic effects documented in [9]: extended-spectrum resistance 51, 173, 237, 240, 39, 164, 104, 238, 153, 265, 92, 224; inhibitor resistance 165, 69, 275, 276, 244, 201; inhibitor and extended-spectrum resistance: 182, 268. Image created with CytoScape [78].