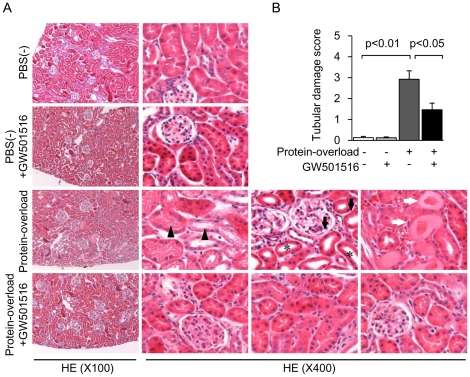
Figure 1. GW501516 attenuates renal proximal tubular cell damage in a protein-overload mouse renal injury model.
(A) Representative HE staining of kidney sections from four groups [PBS(−), PBS(−) + GW501516, Protein-overload and Protein-overload + GW501516]. In the kidney of the protein-overload group, diffused tubular cell vacuolation (black triangles), tubular cell flattening (black arrows), tubular lumen dilation (asterisks) and cast formation (white arrows) were observed (magnification ×100 and ×400). (B) Tubulointerstitial damage scores of kidney sections from four groups. Data are shown as means ± SEM of each individual group.