Figure 10. Proposed mechanism underlying the GW501516-mediated anti-inflammatory effect in proximal tubular cells in proteinuric kidney diseases.
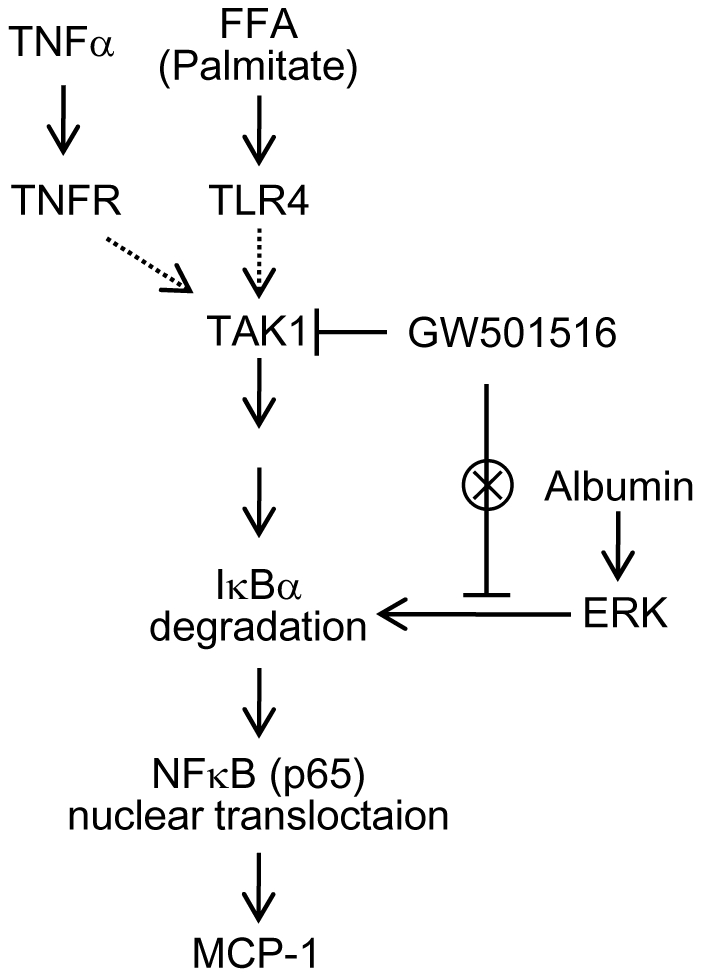
Both TNFα and palmitate induce the phosphorylation of TAK1 in a receptor dependent manner. The phosphorylation of TAK1 activates the NFκB pathway via degradation of IκB. The p65 subunit of NFκB translocates into the nucleus, upregulates the transcription of the pro-inflammatory gene, MCP-1, and causes inflammation. GW501516 can inhibit the phosphorylation of TAK1, but not of MAPKs (including ERK), and the activation of the NFκB-associated inflammatory response in proximal tubular cells. TNFα: tumor necrotic factor α; TNFR: TNFα receptor; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; IKK: IκB Kinase; FFA: free fatty acid; MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein-1.
