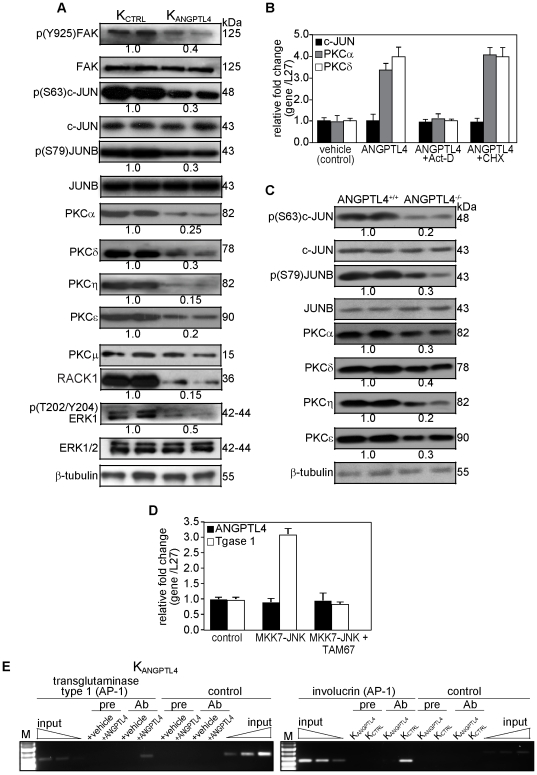
Figure 4. ANGPTL4 modulates the expression of PKCs and activities of AP-1.
(A and C) Representative immunoblot analysis of indicated proteins from (A) epidermis of KCTRL- and KANGPTL4-derived OTCs or (C) skin biopsies of ANGPTL4+/+ and ANGPPTL4−/− mice. Values below immunoblot bands represent the mean fold differences in protein expression levels when compared with either KCTRL (for A) or ANGPTL4+/+ (for C), which was assigned the value one, from 3 independent experiments. β-tubulin serves as a loading and transfer control. (B) Relative fold change in mRNA levels of c-JUN, PKCα and PKCδ in control (KCTRL) human keratinocytes treated with either DMSO vehicle or recombinant ANGPTL4 (6 µg/ml), in the absence or presence of RNA synthesis (actinomycin D, Act-D) or protein synthesis (cycloheximide, CHX) inhibitors as determined by quantitative real-time PCR. Act-D and CHX treatment alone did not affect the transcript level. (D) Relative fold change in mRNA levels of ANGPTL4 and transglutaminase type I in human keratinocytes transiently transfected with expression vectors encoding for either MMK7-JNK or TAM67. Empty expression vector was used a scontrol. Ribosomal protein L27 was used as a normalizing reference gene. Values are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (E) Chromatin immunoprecipitations were done either with vehicle (PBS)- and recombinant ANGPTL4-treated KANGPTL4 or with KCTRL and KANGPTL4 keratinocytes using pre-immune IgG (pre), antibody against phospho-cJUN and phospho-JUNB (Ab). The AP-1 binding site in the human transglutaminase type 1 and involucrin promoter region were immunoprecipitated and specifically amplified using phospho-cJUN and phospho-JUNB, respectively. No amplified signal was obtained in vehicle-treated KANGPTL4, KANGPTL4 or using pre-immune IgG. A control region upstream of the AP-1 binding site served as negative control. Aliquots of the chromatin were also analyzed before immunoprecipitation (input). M: 100-bp DNA marker.