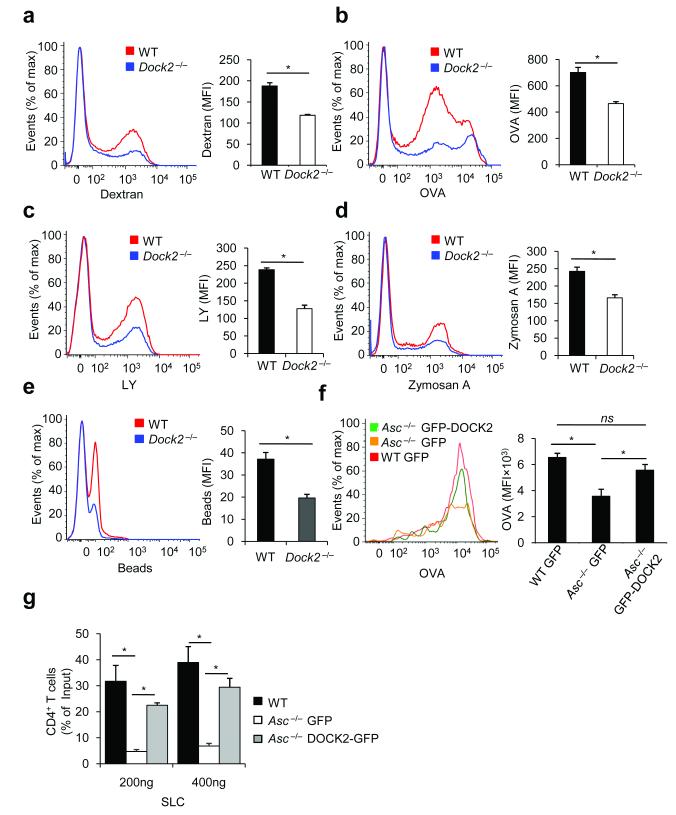
Figure 6. DOCK2 is critical for antigen uptake by dendritic cells, and restores immune cell functions in the absence of ASC.
(a–c) WT and Dock2−/− bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) were incubated for 3 h at 37° C with FITC-labeled OVA (a), dextran (b) or LY (c). After incubation and washing, macropinocytosis was measured by flow cytometry. Results represent mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± S.E. of triplicates of at least three independent experiments. (d–e) WT and Dock2−/− BMDCs were incubated for 3 h at 37° C with fluorescein-labeled zymosan A (d) or polystyrene beads (e). After incubation and washing, phagocytosis was analyzed by flow cytometry. Results represent mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± S.E. of triplicates of at least three independent experiments. (f) WT and Asc−/− BMDCs were nucleofected with GFP- or GFP-DOCK2-expressing plasmids. Macropinocytosis of fluorescein-labeled ovalbumin (OVA) was determined 24h post-transfection by flow cytometry. Results represent mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± S.E. of triplicates of at least three independent experiments. (g) Migration of WT and Asc−/− CD4+ T lymphocytes expressing either GFP or GFP-DOCK2 was analyzed in vitro towards SLC in a transwell chemotaxis assay. Data represent means ± s.d. of triplicates of three independent experiments and are expressed as the percentage of the total T cell population migrating across the transwell.*P-values <0.05 were considered significant (a-g). Non-significant (ns).