Fig. 8.
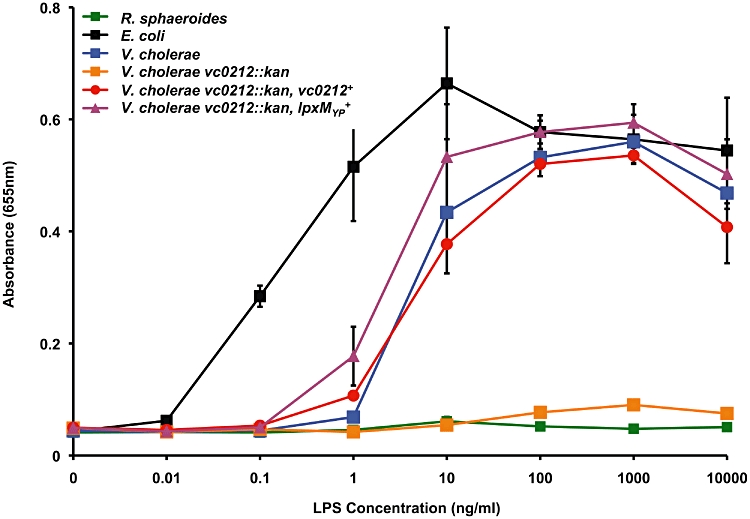
LPS from vc0212 deletion mutant does not stimulate innate immune recognition by human TLR4-MD2. HEK-293 cells transfected with hTLR4-MD2 and co-receptor hCD14 were treated overnight using 10-fold dilutions of highly purified LPS isolated from the indicated strains of V. cholerae. Additionally, LPS from R. sphaeroides (green line) and E. coli (black line) was utilized as negative and positive controls, respectively. Values are the mean of results from triplicate wells ± standard deviation. LPS isolated from the wild-type V. cholerae O1 El Tor (blue line) was found to stimulate TLR4-dependent NF-κB activation in HEK cells, similarly to the positive control (black line). However, LPS isolated from the vc0212 deletion mutant (orange line) did not elicit TLR4-dependent NF-κB activation. LPS isolated from the vc0212 deletion mutant complemented with either vc0212 (red line) or the Y. pestis acyltransferase (magenta line) fully restored TLR-4 stimulation of NF-κB. Wild-type LPS and LPS isolated from complemented strains at 1.0–1000 ng ml−1 showed a significant increase (P ≤ 0.006) in hTLR4-MD2 activation of NF-κB when compared with LPS isolated from the vc0212 deletion mutant. This figure is available in colour online at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com.
