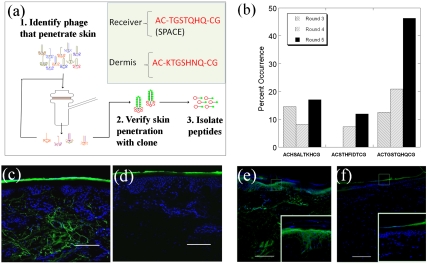
Fig. 1.
The identification of skin penetrating peptides through in vitro phage display in porcine skin. (A) Phage library was applied in the donor compartment of an FDC. Phage found to penetrate through skin into the receiver compartment were collected, amplified, and used for the subsequent rounds of screening. The skin penetrating ability of individual clones was confirmed through diffusion experiments and confocal microscopy. To confirm the peptide’s ability to penetrate skin, the peptide was isolated from the phage and its penetration into skin was confirmed visually through confocal microscopy. (B) Percentage of occurrence for each high frequency peptide sequence from rounds 3 through 5 of the phage display screen. (C and D) Confocal microscopy images of the skin penetration profiles of SPACE and control peptide into porcine skin, respectively. (E and F) Skin penetration profiles of Alexa Fluor 488 labeled streptavidin conjugated to biotinylated SPACE peptide and Alexa Fluor 488 streptavidin alone, respectively. Insets show zoomed in views of the sections highlighted in the main images. Scale bar: 200 µm.