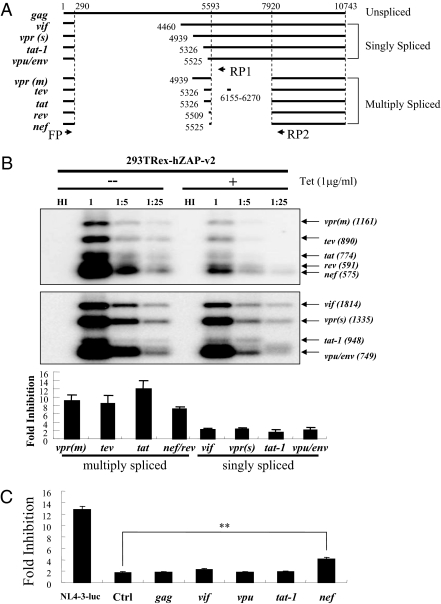
Fig. 3.
(A) Schematic representation of HIV-1 mRNAs expressed from NL4-3-luc. Primers FP and RP1 were used for PCR amplification of cDNAs from singly spliced mRNAs. Primers FP and RP2 were used for PCR amplification of cDNAs from multiply spliced mRNAs. The primers are represented by arrows. (B) 293TREx-hZAP-v2 cells were infected with VSV-G–pseudotyped NL4-3-luc at the indicated dilutions. At 3 h after infection, the cells were mock treated or treated with 1 μg/mL tetracycline. At 48 h after infection, cytoplasmic RNA was extracted. The levels of the mRNAs indicated were analyzed by RT-PCR followed by Southern blotting and quantified by phosphorimaging. Fold inhibition was calculated as the ratio of the mRNA level in mock-treated cells to that in tetracycline-treated cells. Data presented are means ± SE of the fold inhibition values from infections with undiluted or fivefold diluted virus. (C) 293TREx-hZAP-v2 cells were infected with VSV-G–pseudotyped NL4-3-luc, HR′-CMV-Luc virus (Ctrl), or HR′-CMV-Luc virus containing the 5′ UTR from the indicated HIV-1 mRNAs. At 3 h after infection, cells were mock treated or treated with 1 μg/mL tetracycline. Cells were lysed, and luciferase activities were measured at 48 h after infection. Fold inhibition was calculated as the ratio of the luciferase activity in mock-treated cells to that in tetracycline-treated cells. Data presented are means ± SD of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01.