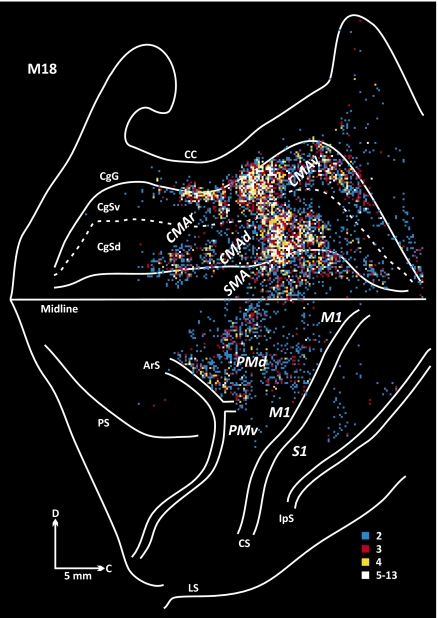
Fig. 4.
Origin of projections to lobule VIII of the vermis (M18). The frontal lobe is displayed with the medial wall of the hemisphere reflected upwards. The map begins at the frontal pole and continues caudally to the intraparietal sulcus (IpS). The cingulate sulcus is unfolded to display the location of labeled neurons on its dorsal (CgSd) and ventral (CgSv) banks. Colored bins indicate the number of labeled neurons in 200-μm bins throughout the cerebral cortex. The number of cells per bin was divided into five levels that are color-coded: white, top 5% of bins (95–100%); yellow, 90–95%; red, 80–90%; and blue, 40–80%. Bins containing 0–40% of cells are omitted. ArS, arcuate sulcus; C, caudal; CC, corpus callosum; CgG, cingulate gyrus; CgSd, cingulate sulcus, dorsal bank; CgSv, cingulate sulcus, ventral bank; CMAd, dorsal cingulate motor area; CMAr, rostral cingulate motor area; CMAv, ventral cingulate motor area; CS, central sulcus; D, dorsal; IpS, intraparietal sulcus; LS, lateral sulcus; M1, primary motor cortex; PMd, dorsal premotor area, PMv, ventral premotor area; S1, primary somatosensory cortex; SMA, supplementary motor area.