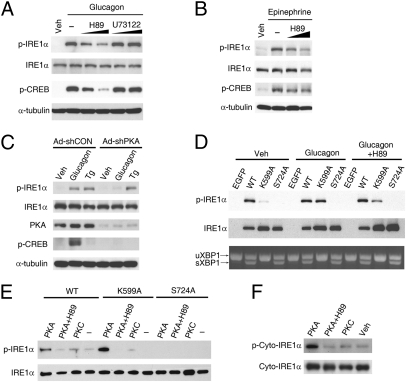
Fig. 3.
PKA is directly responsible for phosphorylating IRE1α. (A and B) Inhibition of PKA decreased glucagon- or epinephrine-induced phosphorylation of IRE1α. (A) Primary hepatocytes precultured for 30 min with PKA inhibitor H89 (at 5 and 10 μM) or PLC inhibitor U73122 (at 5 and 15 μM) were treated with 100 nM glucagon or PBS/DMSO (Veh) for 1 h. (B) Hepatocytes precultured with 5 and 10 μM H89 were stimulated with 10 μM epinephrine for 10 min. Immunoblotting was performed with the indicated antibodies. (C) PKA knockdown blunted glucagon-stimulated IRE1α phosphorylation. Hepatocytes infected for 72 h with adenoviruses Ad-shCON or Ad-shPKA were subsequently incubated for 1 h with 100 nM glucagon or 1 μM Tg. (D) Glucagon-induced phosphorylation of IRE1α was independent of its capability of autophosphorylation. Hepatocytes were infected with adenoviruses expressing EGFP, Flag-tagged human wild-type (WT) IRE1α or IRE1α-K599A and IRE1α-S724A mutants. Cells with or without preincubation for 30 min in 10 μM H89 were then treated with 100 nM glucagon for 1 h. Phosphorylation of IRE1α and splicing of Xbp1 mRNA were analyzed. (E and F) PKA directly phosphorylated IRE1α in vitro. (E) Hepatocytes were infected for 48 h with adenoviruses expressing the indicated forms of Flag-tagged IRE1α. IRE1α proteins were immunoprecipitated with Flag antibody and subsequently incubated with purified mouse PKA or human PKCε at 30 °C for 1 h. (F) Purified recombinant protein of the cytoplasmic portion of human IRE1α was likewise incubated with PKA or PKC. Phosphorylation of IRE1α was analyzed by immunoblotting. All results are shown as representative of three (A–E) or two (F) independent experiments.