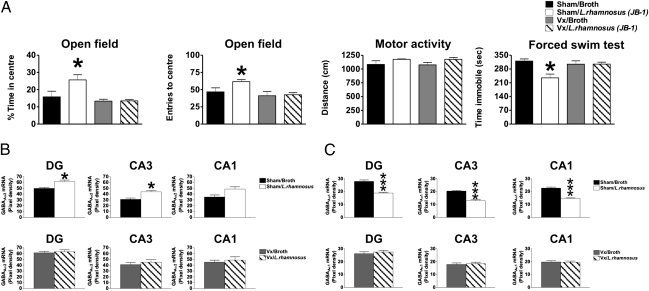
Fig. 4.
Effect of vagotomy (Vx) on anxiety and depression-like behaviors and GABAA subunit expression of animals treated with L. rhamnosus (JB-1). (A) Sham/L. rhamnosus (JB-1) treated mice (n = 10) (white bars) spent more time in the central area of an open field arena in comparison with sham/broth animals (n = 10) (black bars). This behavior is reflected in the number of entries into the central area of the open field with sham/L. rhamnosus (JB-1) mice (n = 10) performing significantly more entries into this area than sham/broth treated animals. These behaviors are prevented by Vx. These differences are not due to an effect on locomotion, as the distance travelled within the open field is no different between the experimental groups. In the FST sham/L. rhamnosus (JB-1) (n = 10) mice spent less time immobile than sham/broth animals (n = 10) an effect prevented by Vx. (B) Sham/L. rhamnosus (JB-1) mice (n = 6) have significantly higher levels of GABAAα2 mRNA expression in the DG and CA3 areas in comparison with sham/broth animals (n = 6). No significant differences were observed in CA1 between the same experimental groups. Vx prevented any further effect of L. rhamnosus (JB-1) on hippocampal GABAAα2 mRNA expression in the DG CA3 and CA1. (C) Sham/L. rhamnosus (JB-1) (n = 6) mice have significantly lower levels of GABAAα1 mRNA in the DG, CA3, and CA1 in comparison with sham/broth (n = 6) animals. Vx prevented any effect of L. rhamnosus (JB-1) on hippocampal GABAAα1 mRNA expression in the DG, CA3, and CA1 areas in the two experimental groups. (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001).