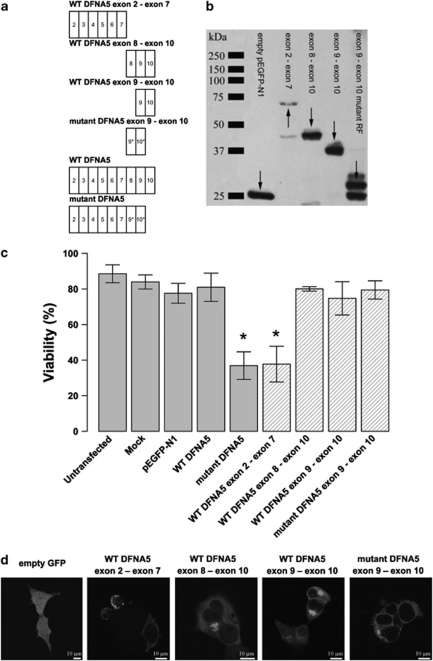
Figure 1.
(a) Graphical representation of the insert content in relation to the construct's name. An exon is indicated by a rectangle containing the relevant exon number. The alternative reading frame used in the aberrant tail of mutant DFNA5 is indicated with an asterisk. (b) Western blot analysis of selected DFNA5 constructs demonstrating that all constructs are expressed when transfected in HEK293T cells (using a pEGFP-N1 vector). Arrows point to the relevant position of the fusion proteins. Some degradation products are visible in lanes 2, 3 and 5. (c) Cell viability measurements 21 h post-transfection. Graphical bars represent the percentage of viable cells. An asterisk denotes statistically significant differences (P<0.05) between transfections with the construct of interest and the WT construct. Control measurements are depicted in light gray colored bars, while constructs specific for this experiment are indicated with hatched bars. This series of transfections demonstrates that the toxic part of DFNA5 is located in the first part of DFNA5. Interestingly, this indicates that the motif that is responsible for toxicity is shared by WT and mutant DFNA5. (d) Subcellular localization of EGFP fusion proteins in HEK293T cells. Transfection of empty pEGFP-N1 vector results in an evenly distributed expression pattern throughout the cytosol. The first part of DFNA5 (exon 2–exon 7) is localized mainly at the plasma membrane. Cell blebbing is seen in cells transfected with this construct. A similar pattern was observed when mutant DFNA5 was transfected in HEK293T cells.7 Both WT DFNA5 exon 8–exon 10 and WT DFNA5 exon 9–exon 10 are localized in the cytoplasm, near the nucleus. Cells transfected with the mutant DFNA5 exon 9–exon 10 construct show expression in the endoplasmic reticulum (see also Supplementary Figure 1). A full color version of this figure can be found in the html version of this paper.