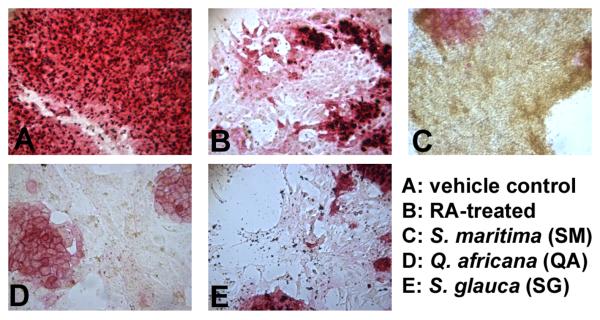
Figure 1. Alkaline phosphatase staining of murine embryonic stem cells.
Cells were treated with semi-purified fractions of plant extracts. Fractions were dried completely, resuspended in DMSO, and diluted in culture medium to final concentrations (1, 5, 10 and 50 μg/ml) and a DMSO concentration ≤ 0.1%. After 96 h treatment, cells were stained and compared to (A) vehicle control (0.01 % DMSO) and (B) 1 μM RA-treatment. Alkaline phosphatase activity decreases rapidly with the onset of differentiation, which can be seen in B-E. Pictured are cells treated with (C) the ethyl acetate fraction of leaf and stem extracts of Suriana maritima (50 μg/ml); (D) the aqueous fraction of leaf extracts from Q. africana (50 μg/ml); and (E) the butanol fraction of wood extract from S. glauca saplings (5 μg/ml). Experiments were performed in duplicate wells with at least 3 independent biological replicates.