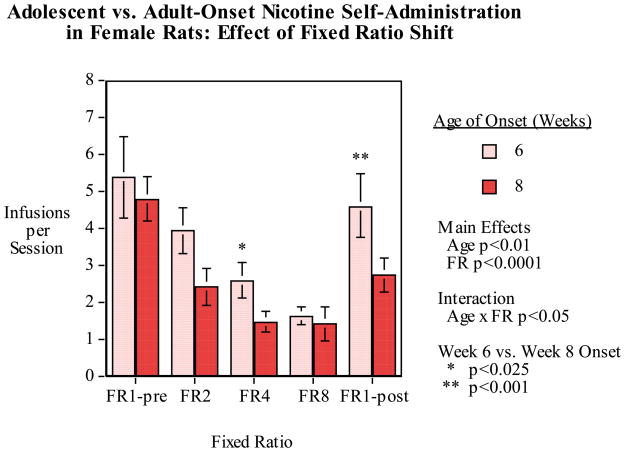
Figure 6.
Six vs. eight-week old age of onset of nicotine self-administration fixed-ratio (FR) progression and reversal, infusions (mean±sem) per 45-min. session in female rats. There were significant main effects of age of onset (p<0.05) and FR (p<0.0001) with younger rats and lower FR resulting in higher levels of nicotine self-administration. There was also a significant age-of-onset × FR interaction (p<0.05) and analysis of the simple main effects at each FR condition showed that the rats that had onset of nicotine access at six weeks of age self-administered significantly more nicotine at FR4 (p<0.025) and the FR1-post conditions (p<0.001).