Figure 4.
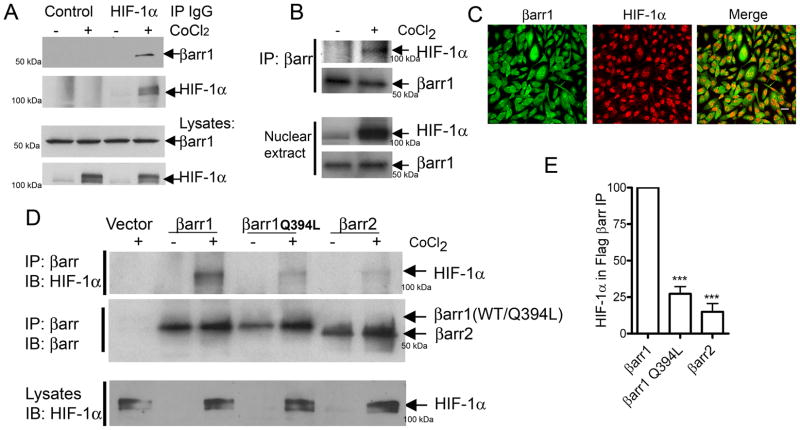
A) MDAMB-231 cells were treated with vehicle or CoCl2 for 6h and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with normal mouse IgG (control) or with anti-HIF-1α mouse monoclonal IgG (28b, SantaCruz Biotech) and the immunoprecipitates (IPs) were probed for bound β-arrestin1. The blots are representative of three independent experiments. B) Nuclear β-arrestin1 from untreated or CoCl2-treated cells (MDAMB-231) was immunoprecipitated with an anti-βarr antibody (K-16, SantaCruz Biotech) and the IPs were probed with anti-HIF-1α antibody. Representative blots are shown from one of two similar experiments. C) Confocal images depict immunostaining for β-arrestin1 (green) and HIF-1α (red) in MDAMB-231 cells treated with CoCl2. (scale bar = 20 μm). D) MDAMB-231 cells were transfected with indicated plasmids encoding Flag-tagged β-arrestins. The top panel shows the amount of HIF-1α bound to Flag-βarr IPs. The middle panel shows the amount of βarr in each IP sample. Lowest panel displays detection of HIF-1α in CoCl2-treated lysate samples. E) HIF-1α in βarr IP was quantified and normalized to βarr levels. *** p < 0.001, versus βarr1, Bonferroni post test, one-way ANOVA, n=4.