Figure 4. SAMHD1 inhibits HIV-1 infection in macrophages.
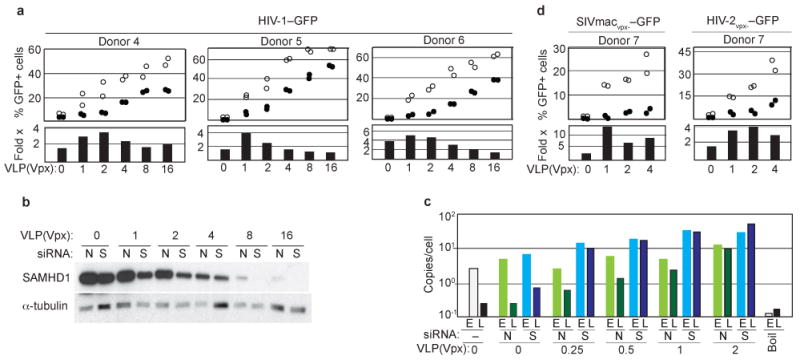
a. RNAi mediated SAMHD1 depletion relieves inhibition of HIV-1 infection in MDM. CD14+ monocytes isolated from three donors were infected with decreasing doses of Vpx-loaded SIV VLP, differentiated into MDM, subjected to RNAi targeting SAMHD1 (open circles), or non-targeting RNAi (filled circles), and infected with HIV-1–GFP reporter virus. GFP+ MDM were quantified 3 days later (upper panels). Fold-stimulation (Fold x) of HIV-1–GFP transduction of MDM, following RNAi targeting SAMHD1, compared to non-targeting RNAi, is also shown (bottom panels).
b. SAMHD1 and α-tubulin control levels in MDM from a typical experiment shown in panel (a). N – non-targeting RNAi, S – RNAi to SAMHD1.
c. SAMHD1 depletion relieves HIV-1 cDNA synthesis. “early” (E) and “late” (L) viral cDNA products in MDM exposed to low doses of Vpx-loaded SIV VLP and transfected with siRNA to SAMHD1 (S) or non-targeting siRNA (N), and then challenged with HIV-1–GFP. (Boil): boiled HIV-1/SIV VLP control.
d. SAMHD1 inhibits MDM transduction by vpx-defective HIV-2vpx-–GFP and SIVmacvpx-–GFP single cycle reporter viruses.
