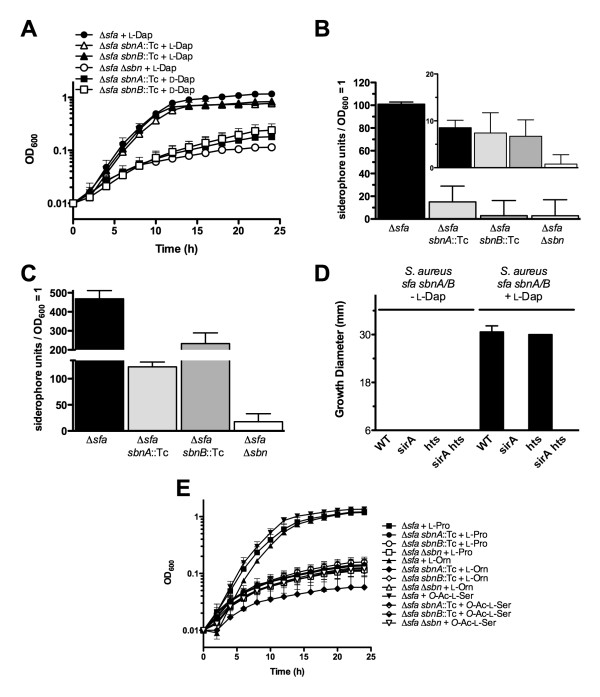
Figure 2.
Supplementation of culture medium with L-Dap allows S. aureus sbnA and sbnB mutants to overcome the block in synthesis of staphyloferrin B. A) Bacterial growth curves in chelex 100-treated TMS containing 10 μM holo-transferrin as the sole iron source, with the indicated supplements. B) Siderophore quantification from culture supernatants of iron-starved S. aureus mutants via CAS assay (see Materials and Methods). The inset graph represents culture supernatants from identical strains but grown in medium supplemented with FeCl3. Siderophore units are normalized to culture density. C) Same as in B) except culture media was supplemented with L-Dap. D) Siderophore-disk diffusion assays. Culture supernatants to be tested were derived from S. aureus Δsfa sbnA::Tc or Δsfa sbnB::Tc strains cultured in medium supplemented with, or without, L-Dap, as indicated, and were spotted onto sterile paper disks before being placed onto TMS agar plates seeded with S. aureus wild-type and siderophore transport mutants, as indicated. Plate disk bioassay is described in Materials and Methods. E) Bacterial growth curves for cultures of S. aureus Δsfa sbnA::Tc and S. aureus Δsfa sbnB::Tc mutants in chelex 100-treated TMS medium containing 10 μM holo-transferrin as the sole iron source, where the medium was supplemented with various hypothesized L-Dap synthase substrates and by-products from Fig. 3, scheme A.