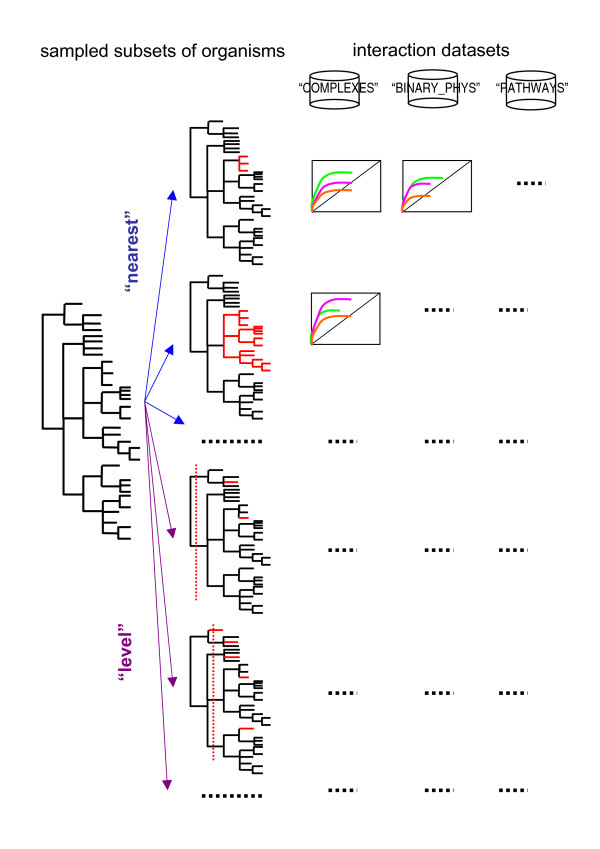
Figure 1.
Schema of the methodology.From an initial set of organisms with completely sequenced genomes (left), a number of subsets (red) are constructed according with two taxonomic criteria: "nearest" (blue) - following the taxonomy of the reference organism (E coli K12) back to the root of the taxonomic tree, all the genomes belonging to each node visited (E coli species, Enterobacteriaceae family, etc.) are taken; "level" (purple) - the tree is successively cut at each taxonomic level (superkingdom, phylum, ...) and one organism is taken from each one of the resulting groups (the one with the largest proteome). On the other hand, a number of "gold standard" interaction datasets representing physical and functional interactions of different nature are used (top). For each combination interaction dataset/organism subset, the performance of the three mirrortree-based methodologies is assessed with a partial-ROC analysis (colored curves).