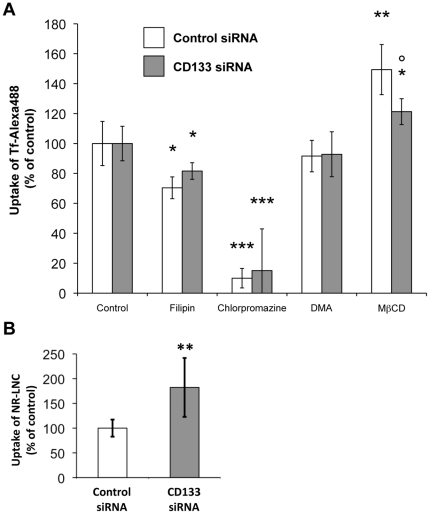
Figure 3. Implication of CD133 in endocytosis mainly involved the clathrin pathway.
A) Consequences of CD133-specific siRNA knockdown for the effectiveness of chemical modulators of known endocytic pathways in modulating Tf uptake by non-differentiated Caco-2 cells. After treatment with either vehicle alone (control), filipin, chlorpromazine, DMA or MβCD added with lovastatin (MβCD), CD133high (control siRNA) and CD133low (CD133 siRNA) non-differentiated Caco-2 cells were exposed to 5 µg/mL Tf-Alexa 488. Cellular internalization of Tf-Alexa 488 was then monitored by flow cytometry. Results are expressed as a % of Tf-Alexa 488 amounts that were internalized in the vehicle treated control. Note the absence of effect of CD133-siRNA knockdown on the major inhibition of Tf-uptake caused by chlorpromazine. Note also the reduced up regulatory effect of cholesterol extraction in the CD133 low situation (MβCD). Data represented mean ± s.e.m. of a triplicate obtained from one representative experiment that was reproduced twice. Comparisons with control: Dunnett's test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001; comparison between control siRNA and CD133 siRNA: Dunnett's test: p<0.05. B) Specific siRNA mediated knockdown of CD133 within non-differentiated Caco-2 cells led to an increase in LNC intracellular accumulation. Flow cytometric analysis of intracellular uptake of NR-LNC within CD133high (Control siRNA) and CD133low (CD133 siRNA) Caco-2 cells after 1 h of incubation at 37°C/5%CO2. Results are expressed as percentage of control, thus representing the geomean fluorescence intensity levels obtained for cells treated with vehicle alone. Data represented mean ± s.e.m. obtained from three independent experiments. Dunnett's test: **p<0.01.