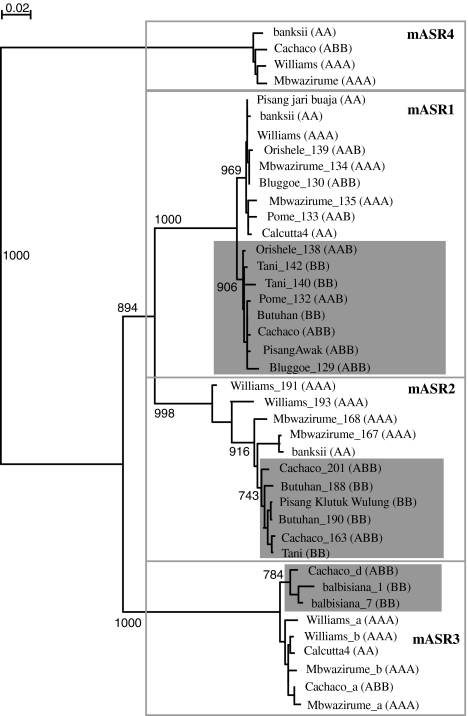
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic relationship between mAsr genomic sequences in various wild and cultivated accessions of Musa. Full-length genomic sequences (including the intron) were aligned using ClustalX and a neighbor-joining tree was constructed (bootstrap of 1,000). The distance between sequences is indicated by branch length. Bootstrap values between major groups and >75% are indicated. Gray boxes indicate putative sub-clusters associated with the A and B genomes for mAsr1, mAsr2 and mAsr3. For each sequence, the name of the cultivar or wild variety is indicated and the genome composition in brackets. Sequences from the same cultivar or wild variety are distinguished by the name of the clone corresponding to each particular sequence. The gene ID of each of the genes used for the construction of this tree can be found in Online Resource 1