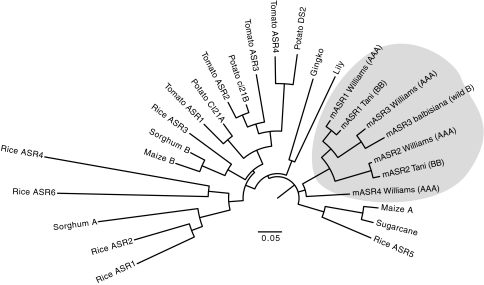
Fig. 3.
Neighbor-joining tree of ASR protein sequences from various plants species. Full-length protein sequences were aligned using ClustalX and an unrooted neighbor-joining tree was constructed (bootstrap of 1,000). The distance between sequences is indicated by branch length. The four members of the mAsr family are enclosed in the gray box and represented by sequences from ‘Williams’ (AAA, mASR1_clone173, mASR2_clone193, mASR3_clone_a and mASR4_clone170), ‘Tani’ (BB, mASR1_clone140, mASR2_clone197) and balbisiana (BB, mASR3_clone1). Sequences from other plant species are available in NCBI: NP_001152333.1 (Maize B), XP_002447825.1 (Sorghum B), XP_002457802.1 (Sorghum A), AAT57940.1 (Sugarcane), CAA72998.1 (Maize A), ACZ50736 (mASR4), ACZ60133.1 (mASR1), ACZ60138.1 (mASR1), ACZ50744.1 (mASR2), ACZ50739.1 (mASR2), EEC72202 (Rice ASR2), NP_001045487 (Rice ASR6), BAD28236 (Rice ASR3), NP_001173936 (Rice ASR4), NP_001065841 (Rice ASR5), NP_001045459 (Rice ASR1), 2282019 (Tomato ASR1), 584787 (Tomato ASR2), 400471 (Tomato ASR3), AAY98032 (Tomato ASR4), 4098248 (Potato CI21A), 4098250 (Potato ci21B), 23095773 (Potato DS2), 6525055 (Lily) and 38532363 (Gingko). The nomenclature of the Rice ASR proteins comes from (Philippe et al. 2010)