Figure 1.
BIK1 Conserved Residues and in Vitro and in Vivo Kinase Assays.
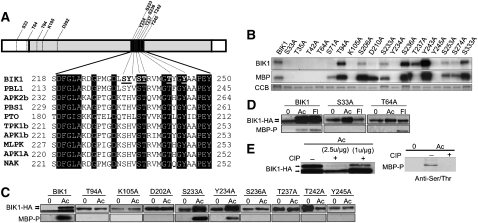
(A) Structure of the BIK1 protein and comparison of residues in the ADs of BIK1 and related kinases. Gray region denotes the KD and black the AD. Residues noted in the BIK1 protein indicate those substituted for in planta assays.
(B) Kinase activity of recombinant BIK1 and Ala substitution mutants produced in E. coli detected by autoradiogram. CCB, Coomassie blue staining.
(C) and (D) BIK1 substitution mutants in vivo detected by a mobility shift on an HA-immunoblot or by phosphoserine/Thr-specific antibody.
(E) BIK1 and MBP phosphorylation is abrogated by phosphatase treatment. Protein dephosphorylation was performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol (New England Biolabs) with ~1 to 2.5 units CIP/μg protein (left) or (~2.5 μ/μg) (right). −, Buffer; +, CIP.
In (C) and (D), plants were treated with ACC (Ac) or flg22 (Fl) for 3 h and assayed for changes in BIK1 and MBP phosphorylation activity. In (C) to (E), in vivo BIK1 phosphorylation was detected by ACC or flagellin-induced mobility shifts observable by HA-immunoblot. The top band corresponds to phosphorylated BIK1, which is migrating slower than the unphosphorylated form. MBP phosphorylation by BIK1 was detected by immunoblots with a phosphoserine/Thr-specific antibody.