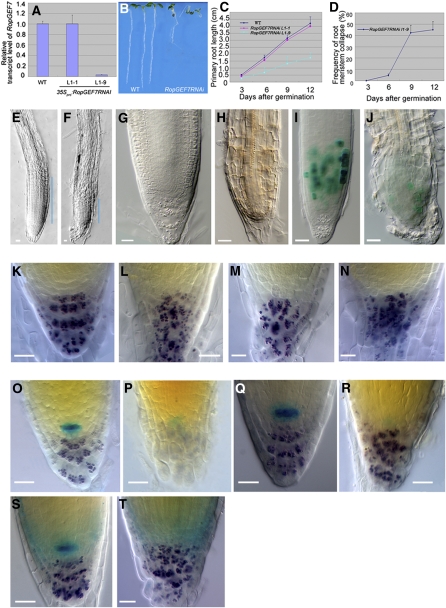
Figure 3.
RopGEF7 Is Important for Root Stem Cell Maintenance.
(A) qRT-PCR analysis of RopGEF7 expression in 7-d-old wild-type and RopGEF7 RNAi transgenic lines (L1-1 and L1-9).
(B) Phenotype of 5-d-old seedlings of the wild type and RopGEF7RNAi (from left to right).
(C) and (D) Root length (C) and meristem collapse frequency (D) at different time points for the wild type and RopGEF7RNAi. In each experiment, a total of 30 to 50 plants was used for measurement. Data presented in (D) are the averages from three biological repeats with sd and with 50 plants in each repeat.
(E) and (F) Three-day-old root tips of the wild type (E) and RopGEF7RNAi (F). Blue lines indicate the RM region.
(G) and (H) Nine-day-old root tips of the wild type (G) and RopGEF7RNAi (H).
(I) and (J) Cyclin B1;1:GUS expression in 5-d-old root tips of the wild type (I) and RopGEF7RNAi (J).
(K) to (N) Distal RM region of 5-d-old seedling of the wild type (K) and RopGEF7RNAi ([L] to [N]). Starch granule staining labels the differentiated cells in the columella (purple).
(O) and (P) Double staining of QC25:GUS marker and starch granules (purple) in 5-d-old wild-type (O) and RopGEF7RNAi (P) seedlings.
(Q) and (R) Double staining of QC46:GUS marker and starch granules in 5-d-old root tips of wild-type (Q) and RopGEF7RNAi (R) seedlings.
(S) and (T) Double staining of RopGEF7pro:GUS marker and starch granules in 5-d-old root tips of wild-type (S) and RopGEF7RNAi (T) seedlings.
Bars = 20 μm in (E) to (T).