Figure 6.
vps2.1 Homozygous Mutants Are Embryo Lethal.
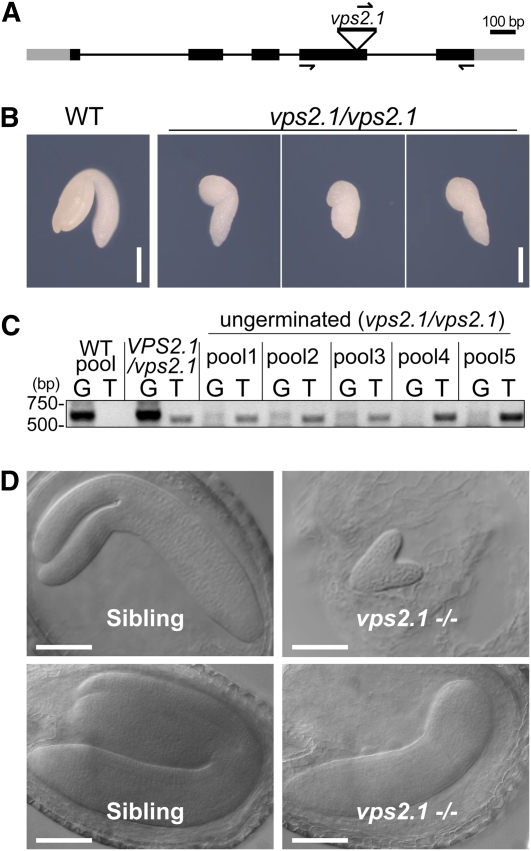
(A) T-DNA insertion and primer binding site in VPS2.1. Lines indicate introns and boxes indicate exons (black boxes, coding region; gray boxes, untranslated regions). The position of the T-DNA in the vps2.1 mutant is shown.
(B) Photographs of wild-type (WT) and vps2.1 homozygous embryos dissected from dry seeds. Bars = 0.2 mm.
(C) PCR analysis of wild-type and vps2.1 homozygous mutant embryos. Twenty embryos were dissected from the ungerminated seeds of a VPS2.1/vps2.1 self-pollinated plant, and total DNA was extracted from pools of four embryos. DNA extracted from a pool of four wild-type embryos, and DNA from a VPS2.1/vps2.1 heterozygous plant was used as control. PCR was performed with either gene-specific forward and reverse primers (G lanes) or a T-DNA left border primer in combination with the gene-specific reverse primer (T lanes). Note that all ungerminated seeds contain embryos homozygous for the T-DNA insertion. The primers used for genotyping and their sequences are presented in Methods and Supplemental Table 3 online.
(D) vps2.1 homozygous mutant embryos (right panels) are delayed in embryogenesis in comparison to their wild-type-looking siblings (left panels). Bars = 100 μm.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]